Evaluation of the Optic Nerve Head in Glaucoma
- PMID: 26997792
- PMCID: PMC4741153
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10008-1146
Evaluation of the Optic Nerve Head in Glaucoma
Abstract
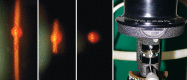
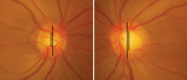
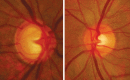
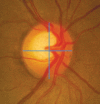
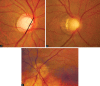
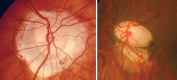
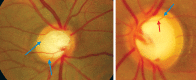
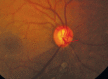
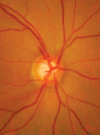
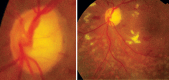
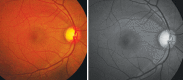
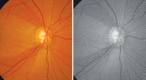
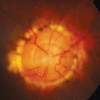
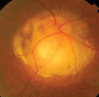
Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy leading to changes in the intrapaillary and parapaillary regions of the optic disk. Despite technological advances, clinical identification of optic nerve head characteristics remains the first step in diagnosis. Careful examination of the disk parameters including size, shape, neuroretinal rim shape and pallor; size of the optic cup in relation to the area of the disk; configuration and depth of the optic cup; ratios of cup-to-disk diameter and cup-to-disk area; presence and location of splinter-shaped hemorrhages; occurrence, size, configuration, and location of parapapillary chorioretinal atrophy; and visibility of the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) is important to differentiate between the glaucomatous and nonglaucomatous optic neuropathy. How to cite this article: Gandhi M, Dubey S. Evaluation of the Optic Nerve Head in Glaucoma. J Current Glau Prac 2013;7(3):106-114.
Keywords: Disk anomalies.; Neuroretinal rim; Optic cup; Optic disk; Optic disk hemorrhage; Parapaillary atrophy; Retinal nerve fiber layer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Nangia V, Matin A, Bhojwani K, Kulkarni M, Yadav M, Jonas JB. Optic disc size in a population-based study in central India: the Central India Eye and Medical Study (CIEMS). Acta Ophthalmol. 2008 Feb;86(1):103–104. - PubMed
-
- Sekhar GC, Prasad K, Dandona R, John RK, Dandona L. Planimetric optic disc parameters in normal eyes: a population-based study in South India. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2001 Mar;49(1):19–23. - PubMed
-
- Jonas JB, Gusek GC, Naumann GO. Optic disc, cup and neuroretinal rim size, configuration and correlations in normal eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988 Jul;29(7):1151–1158. - PubMed
-
- Ramrattan RS, Wolfs RC, Jonas JB, Hofman A, de Jong PT. Determinants of optic disk characteristics in a general population. The Rotterdam Study. Ophthalmology. 1999 Aug;106(8):1588–1596. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
