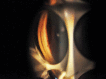Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome
- PMID: 26997794
- PMCID: PMC4741155
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10008-1148
Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome
Abstract
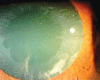
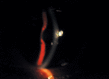
Pseudoexfoliation (PXF) syndrome is a well-recognized clinical entity of considerable clinical significance. It is associated with poor mydriasis, cataracts with weak zonular support, secondary glaucoma and possibly with biochemical abnormalities, such as elevated homocysteine and systemic diseases involving the cardiovascular and central nervous system. There have also been some recent studies identifying mutations in genes which are associated with PXF. How to cite this article: Ariga M, Nivean M, Utkarsha P. Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome. J Current Glau Prac 2013;7(3): 118-120.
Keywords: Homocysteine; Mutations.; Mydriasis; Pseudoexfoliation; Secondary glaucoma; Weak zonules.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Vessani RM, Ritch R, Liebmann JM, Jofe M. Plasma homocysteine is elevated in patients with exfoliation syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003 Jul;136(1):41–46. - PubMed
-
- Prince AM, Ritch R. Clinical signs of the pseudoexfoliation syndrome. Ophthalmology. 1986 Jun;93(6):803–807. - PubMed
-
- Puska P, Vasara K, Harju M, Setälä K. Corneal thickness and corneal endothelium in normotensive subjects with unilateral exfoliation syndrome. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2000 Aug;238(8):659–663. - PubMed
-
- Naumann GO, Schlötzer-Schrehardt U. Keratopathy in pseudoexfoliation syndrome as a cause of corneal endothelial decompensation: a clinicopathologic study. Ophthalmology. 2000 Jun;107(6):1111–1124. - PubMed
-
- Pohjanpelto P. Long-term prognosis of visual field in glaucoma simplex and glaucoma capsular. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1985 Aug;63(4):418–423. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources