Effect of Topical Calcium Channel Blockers on Intraocular Pressure in Steroid-induced Glaucoma
- PMID: 26997802
- PMCID: PMC4741158
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10008-1155
Effect of Topical Calcium Channel Blockers on Intraocular Pressure in Steroid-induced Glaucoma
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the effect of 0.125% verapamil and 0.5% diltiazem eye drops on intraocular pressure (IOP) in steroid-induced glaucoma in rabbit eyes.
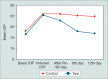
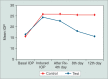
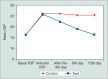
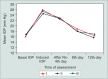
Methods: A total of 18 rabbits with steroid-induced glaucoma were divided into three groups (A, B and C; n = 6 each). Right eyes in groups A, B and C received 0.5% diltiazem, 0.125% verapamil and 0.5% timolol eye drops twice daily for 12 days, respectively; whereas, left eyes received distilled water. IOP was measured with Tono-pen XL at baseline, day 4, day 8, and day 12 of treatment.
Results: Both 0.5% diltiazem and 0.125% verapamil eye drops significantly reduced IOP compared to control eyes (p < 0.05). Reduction of IOP by 0.5% diltiazem, 0.125% verapamil eye drops were comparable to 0.5% timolol. No surface toxicity or systemic side effects were noted during the study period.
Conclusion: Calcium channel blockers, verapamil, and diltia-zem significantly reduced IOP in rabbiteyes. This group of drugs may have a potential role in treatment of glaucoma How to cite this article: Ganekal S, Dorairaj S, Jhanji V, Kudlu K. Effect of Topical Calcium Channel Blockers on Intraocular Pressure in Steroid-induced Glaucoma. J Current Glau Prac 2014;8(1):15-19.
Keywords: Calcium channel blockers; Intraocular pressure; Steroid-induced glaucoma..
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative study of topical application of timolol and verapamil in patients with glaucoma within 6 months.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2009 Dec;25(6):551-3. doi: 10.1089/jop.2009.0005. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2009. PMID: 20028263 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of calcium channel blockers alone and in combination with antiglaucoma medications on intraocular pressure in the primate eye.J Glaucoma. 2000 Aug;9(4):334-9. doi: 10.1097/00061198-200008000-00009. J Glaucoma. 2000. PMID: 10958608
-
The effect of topical diltiazem on the intraocular pressure in betamethasone-induced ocular hypertensive rabbits.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998 Jan;284(1):278-82. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998. PMID: 9435188
-
[A challenge to primary open-angle glaucoma including normal-pressure. Clinical problems and their scientific solution].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2012 Mar;116(3):233-67; discussion 268. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2012. PMID: 22568103 Review. Japanese.
-
Topical dorzolamide 2%/timolol 0.5%: a review of its use in the treatment of open-angle glaucoma.Drugs Aging. 2000 Dec;17(6):477-96. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200017060-00005. Drugs Aging. 2000. PMID: 11200308 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term corticosteroid-induced chronic glaucoma model produced by intracameral injection of dexamethasone-loaded PLGA microspheres.Drug Deliv. 2021 Dec;28(1):2427-2446. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.1998245. Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 34763590 Free PMC article.
-
Potential neuroprotective biomolecules in ophthalmology.Int Ophthalmol. 2021 Mar;41(3):1103-1109. doi: 10.1007/s10792-020-01634-8. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Int Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33180279 Review.
-
Influence of Trace Elements on Neurodegenerative Diseases of The Eye-The Glaucoma Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 21;22(9):4323. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094323. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systems genetics identifies a role for Cacna2d1 regulation in elevated intraocular pressure and glaucoma susceptibility.Nat Commun. 2017 Nov 24;8(1):1755. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00837-5. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29176626 Free PMC article.
-
Bilateral neovascular glaucoma associated with Radium-223 infusions for prostate cancer.Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2024 Aug 22;36:102142. doi: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2024.102142. eCollection 2024 Dec. Am J Ophthalmol Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39290997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kumarasamy NA, Lam FS, Wang AL, Theoharides TC. Glaucoma: current and developing concepts of infammation, patho-genesis and treatment. Eur J Infamm. 2006 Oct;4(3):129–137.
-
- Kass MA, Heuer DK, Higginbotham EJ, Johnson CA, Keltner JL, Miller JP, Parrish RK 2nd, Wilson MR, Gordon MO. The Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study: a randomized trial determines that topical ocular hypotensive medication delays or prevents the onset of primary open-angle glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002 Jun;120(6):701–713. - PubMed
-
- Ohtsuka M, Yokota M, Kodama I, Yamada K, Shibata S. New generation dihydropyridine calcium entry blockers: in search of greater selectivity for one tissue subtype. Gen Pharmacol. 1989;20(5):539–556. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
