Laricitrin suppresses increased benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung tumor-associated monocyte-derived dendritic cell cancer progression
- PMID: 26998077
- PMCID: PMC4774572
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.4153
Laricitrin suppresses increased benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung tumor-associated monocyte-derived dendritic cell cancer progression
Abstract
Benzo(a)pyrene (BaP) stimulates lung cancer cells, promoting monocyte-derived dendritic cells to secrete soluble factors, including heparin binding-epidermal growth factor and C-X-C motif chemokine 5. The secretions from monocyte-derived dendritic cells stimulate the progression of lung cancer cells, including the migration and invasion of cells. To the best of our knowledge, these secretions remain unknown, and require additional study. The present study identified that treatment with BaP-H1395-tumor-associated dendritic cell-conditioned medium had the most marked effect on cell migration and invasion. This result may be associated with the female gender, stage 2 adenocarcinoma or mutation of the proto-oncogene B-Raf (BRAF), according to the cell line background. Laricitrin, a dietary flavonoid derivative present in grapes and red wine, suppresses certain factors and decreases the progression of lung cancer cells that are promoted by BaP in the lung cancer tumor microenvironment. The results of the present study suggest that prolonged exposure to BaP exacerbates lung cancer, particularly in female lung cancer patients with the BRAF mutation, but that laricitrin may ameliorate this effect.
Keywords: benzo(a)pyrene; laricitrin; lung cancer; tumor microenvironment.
Figures

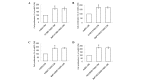
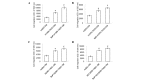
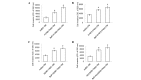

Similar articles
-
Laricitrin ameliorates lung cancer-mediated dendritic cell suppression by inhibiting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 20;7(51):85220-85234. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13240. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27833081 Free PMC article.
-
Benzo(a)pyrene promotes migration, invasion and metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma cells by upregulating TGIF.Toxicol Lett. 2018 Sep 15;294:11-19. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.05.005. Epub 2018 May 7. Toxicol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29746904
-
Benzo(a)pyrene regulated A549 cell migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by up-regulating long non-coding RNA linc00673.Toxicol Lett. 2020 Mar 1;320:37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.11.024. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Toxicol Lett. 2020. PMID: 31778776
-
Benzo[a]pyrene increases DNA double strand break repair in vitro and in vivo: a possible mechanism for benzo[a]pyrene-induced toxicity.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2014 Jan 15;760:64-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2013.12.003. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2014. PMID: 24412381
-
Induction of fibroblast growth factor-9 and interleukin-1alpha gene expression by motorcycle exhaust particulate extracts and benzo(a)pyrene in human lung adenocarcinoma cells.Toxicol Sci. 2005 Oct;87(2):483-96. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfi251. Epub 2005 Jul 7. Toxicol Sci. 2005. PMID: 16002475
Cited by
-
Vaccine-based therapeutic interventions in lung cancer management: A recent perspective.Med Oncol. 2024 Sep 24;41(11):249. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02489-0. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39316239 Review.
-
The Spectrum of Pharmacological Actions of Syringetin and Its Natural Derivatives-A Summary Review.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 4;14(23):5157. doi: 10.3390/nu14235157. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36501187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Laricitrin ameliorates lung cancer-mediated dendritic cell suppression by inhibiting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 20;7(51):85220-85234. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13240. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27833081 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Effects and Molecular Mechanisms of Bioactive Compounds Against Respiratory Diseases: Traditional Chinese Medicine Theory and High-Frequency Use.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 27;12:734450. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.734450. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34512360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ameliorating effect of lipo-ATRA treatment on the expression of TIG3 and its suppressing effect on PPARγ gene expression in lung cancer animal model.Mol Cell Biochem. 2019 Oct;460(1-2):105-112. doi: 10.1007/s11010-019-03574-z. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31300983
References
-
- Kuo CH, Chen KF, Chou SH, Huang YF, Wu CY, Cheng DE, Chen YW, Yang CJ, Hung JY, Huang MS. Lung tumor-associated dendritic cell-derived resistin promoted cancer progression by increasing Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome candidate 1/Twist pathway. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34:2600–2609. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt281. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
