Does influenza A virus infection affect movement behaviour during stopover in its wild reservoir host?
- PMID: 26998334
- PMCID: PMC4785985
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.150633
Does influenza A virus infection affect movement behaviour during stopover in its wild reservoir host?
Abstract
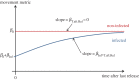
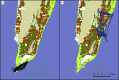
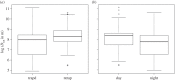
The last decade has seen a surge in research on avian influenza A viruses (IAVs), in part fuelled by the emergence, spread and potential zoonotic importance of highly pathogenic virus subtypes. The mallard (Anas platyrhynchos) is the most numerous and widespread dabbling duck in the world, and one of the most important natural hosts for studying IAV transmission dynamics. In order to predict the likelihood of IAV transmission between individual ducks and to other hosts, as well as between geographical regions, it is important to understand how IAV infection affects the host. In this study, we analysed the movements of 40 mallards equipped with GPS transmitters and three-dimensional accelerometers, of which 20 were naturally infected with low pathogenic avian influenza virus (LPAIV), at a major stopover site in the Northwest European flyway. Movements differed substantially between day and night, as well as between mallards returning to the capture site and those feeding in natural habitats. However, movement patterns did not differ between LPAIV infected and uninfected birds. Hence, LPAIV infection probably does not affect mallard movements during stopover, with high possibility of virus spread along the migration route as a consequence.
Keywords: avian influenza A virus; effect of infection; mallard; movement; stopover; transmission.
Figures
References
-
- Jarosz AM, Davelos AL. 1995. Effects of disease in wild plant-populations and the evolution of pathogen aggressiveness. New Phytol. 129, 371–387. (doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1995.tb04308.x) - DOI
-
- Weatherhead PJ, Bennett GF. 1992. Ecology of parasitism of brown-headed cowbirds by Hematozoa. Can. J. Zool. 70, 1–7. (doi:10.1139/Z92-001) - DOI
-
- Friedman CS, Wight N, Crosson LM, VanBlaricom GR, Lafferty KD. 2014. Reduced disease in black abalone following mass mortality: phage therapy and natural selection. Front. Microbiol. 5, 78 (doi:10.3389/fmicb.2014.00078) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sorci G, Cornet S, Faivre B. 2013. Immunity and the emergence of virulent pathogens. Infect. Genet. Evol. 16, 441–446. (doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2012.12.031) - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

