Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Cerebral Blood Flow in Animal Stroke Models
- PMID: 26998527
- PMCID: PMC4797655
- DOI: 10.4103/2394-8108.178544
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Cerebral Blood Flow in Animal Stroke Models
Abstract
Perfusion could provide useful information on metabolic and functional status of tissue and organs. This review summarizes the most commonly used perfusion measurement methods: dynamic susceptibility weighted contrast (DSC) and arterial spin labeling (ASL) and their applications in experimental stroke. Some new developments of CBF techniques in animal models are also discussed.
Keywords: arterial spin labeling (ASL); dynamic susceptibility weighted contrast (DSC); functional MRI; perfusion MRI.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
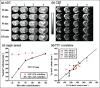
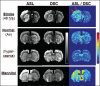
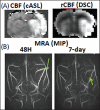
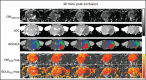
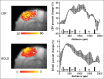
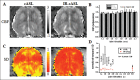


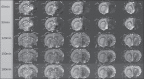

References
-
- Rosen BR, Belliveau JW, Vevea JM, Brady TJ. Perfusion imaging with NMR contrast agents. Magn Reson Med. 1990;14:249–65. - PubMed
-
- Edelman RR, Mattle HP, Atkinson DJ, Hill T, Finn JP, Mayman C, et al. Cerebral blood flow: Assessment with dynamic contrast-enhanced T2*-weighted MR imaging at 1.5 T. Radiology. 1990;176:211–20. - PubMed
-
- Østergaard L. Principles of cerebral perfusion imaging by bolus tracking. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2005;22:710–7. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

