Looking Beyond the Terrestrial: The Potential of Seaweed Derived Bioactives to Treat Non-Communicable Diseases
- PMID: 26999166
- PMCID: PMC4820313
- DOI: 10.3390/md14030060
Looking Beyond the Terrestrial: The Potential of Seaweed Derived Bioactives to Treat Non-Communicable Diseases
Abstract
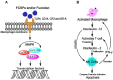
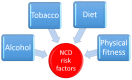
Seaweeds are a large and diverse group of marine organisms that are commonly found in the maritime regions of the world. They are an excellent source of biologically active secondary metabolites and have been shown to exhibit a wide range of therapeutic properties, including anti-cancer, anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic activities. Several Asian cultures have a strong tradition of using different varieties of seaweed extensively in cooking as well as in herbal medicines preparations. As such, seaweeds have been used to treat a wide variety of health conditions such as cancer, digestive problems, and renal disorders. Today, increasing numbers of people are adopting a "westernised lifestyle" characterised by low levels of physical exercise and excessive calorific and saturated fat intake. This has led to an increase in numbers of chronic Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes mellitus, being reported. Recently, NCDs have replaced communicable infectious diseases as the number one cause of human mortality. Current medical treatments for NCDs rely mainly on drugs that have been obtained from the terrestrial regions of the world, with the oceans and seas remaining largely an untapped reservoir for exploration. This review focuses on the potential of using seaweed derived bioactives including polysaccharides, antioxidants and fatty acids, amongst others, to treat chronic NCDs such as cancer, cardiovascular disease and diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: bioactives; cancer; cardiovascular disease; diabetes; fucoidan; non-communicable disease; prebiotics; seaweed; short-chain fatty acids.
Figures





References
-
- Mouritsen O.G., Mouritsen J.D., Johansen M. Seaweeds: Edible, Available, and Sustainable. University of Chicago Press; Chicago, IL, USA: 2013.
-
- Stabili L., Acquaviva M.I., Biandolino F., Cavallo R.A., De Pascali S.A., Fanizzi F.P., Narracci M., Petrocelli A., Cecere E. The lipidic extract of the seaweed Gracilariopsis longissima (Rhodophyta, Gracilariales): A potential resource for biotechnological purposes? New Biotechnol. 2012;29:443–450. doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2011.11.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- López-Mosquera M.E., Fernández-Lema E., Villares R., Corral R., Alonso B., Blanco C. Composting fish waste and seaweed to produce a fertilizer for use in organic agriculture. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011;9:113–117. doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2011.11.018. - DOI
-
- Lola-Luz T., Hennequart F., Gaffney M. Effect on health promoting phytochemicals following seaweed application, in potato and onion crops grown under a low input agricultural system. Sci. Hortic. 2014;170:224–227. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2014.03.022. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

