Different Subsets of T Cells, Memory, Effector Functions, and CAR-T Immunotherapy
- PMID: 26999211
- PMCID: PMC4810120
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers8030036
Different Subsets of T Cells, Memory, Effector Functions, and CAR-T Immunotherapy
Abstract
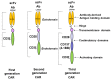
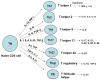
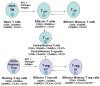
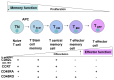
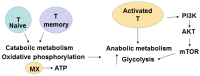
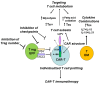
This review is focused on different subsets of T cells: CD4 and CD8, memory and effector functions, and their role in CAR-T therapy--a cellular adoptive immunotherapy with T cells expressing chimeric antigen receptor. The CAR-T cells recognize tumor antigens and induce cytotoxic activities against tumor cells. Recently, differences in T cell functions and the role of memory and effector T cells were shown to be important in CAR-T cell immunotherapy. The CD4⁺ subsets (Th1, Th2, Th9, Th17, Th22, Treg, and Tfh) and CD8⁺ memory and effector subsets differ in extra-cellular (CD25, CD45RO, CD45RA, CCR-7, L-Selectin [CD62L], etc.); intracellular markers (FOXP3); epigenetic and genetic programs; and metabolic pathways (catabolic or anabolic); and these differences can be modulated to improve CAR-T therapy. In addition, CD4⁺ Treg cells suppress the efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy, and different approaches to overcome this suppression are discussed in this review. Thus, next-generation CAR-T immunotherapy can be improved, based on our knowledge of T cell subsets functions, differentiation, proliferation, and signaling pathways to generate more active CAR-T cells against tumors.
Keywords: CD4 T cells; CD8 T cells; cancer; chimeric antigen receptor (CAR); immunotherapy.
Figures
References
-
- Louis C.U., Savoldo B., Dotti G., Pule M., Yvon E., Myers G.D., Rossig C., Russell H.V., Diouf O., Liu E., et al. Antitumor activity and long-term fate of chimeric antigen receptor-positive T cells in patients with neuroblastoma. Blood. 2011;118:6050–6056. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-05-354449. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

