MicroRNA function in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 27000418
- PMCID: PMC5660628
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.03.015
MicroRNA function in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
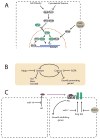
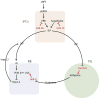
Over the last decade, microRNAs have emerged as critical regulators in the expression and function of animal genomes. This review article discusses the relationship between microRNA-mediated regulation and the biology of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. We focus on the roles that microRNAs play in tissue growth, germ cell development, hormone action, and the development and activity of the central nervous system. We also discuss the ways in which microRNAs affect robustness. Many gene regulatory networks are robust; they are relatively insensitive to the precise values of reaction constants and concentrations of molecules acting within the networks. MicroRNAs involved in robustness appear to be nonessential under uniform conditions used in conventional laboratory experiments. However, the robust functions of microRNAs can be revealed when environmental or genetic variation otherwise has an impact on developmental outcomes.
Keywords: Drosophila; MiRNAs; MicroRNAs.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Gilboa L, Lehmann R. How different is Venus from Mars? The genetics of germ-line stem cells in Drosophila females and males. Development. 2004;131:4895–905. - PubMed
-
- Iovino N, Pane A, Gaul U. miR-184 has multiple roles in Drosophila female germline development. Developmental cell. 2009;17:123–33. - PubMed
-
- Pek JW, Lim AK, Kai T. Drosophila maelstrom ensures proper germline stem cell lineage differentiation by repressing microRNA-7. Developmental cell. 2009;17:417–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

