Prognostic factors and risk stratification in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer receiving docetaxel-based chemotherapy
- PMID: 27001073
- PMCID: PMC4802623
- DOI: 10.1186/s12894-016-0133-y
Prognostic factors and risk stratification in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer receiving docetaxel-based chemotherapy
Abstract
Background: While novel drugs have been developed, docetaxel remains one of the standard initial systemic therapies for castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) patients. Despite the excellent anti-tumor effect of docetaxel, its severe adverse effects sometimes distress patients. Therefore, it would be very helpful to predict the efficacy of docetaxel before treatment. The aims of this study were to evaluate the potential value of patient characteristics in predicting overall survival (OS) and to develop a risk classification for CRPC patients treated with docetaxel-based chemotherapy.
Methods: This study included 79 patients with CRPC treated with docetaxel. The variables, including patient characteristics at diagnosis and at the start of chemotherapy, were retrospectively collected. Prognostic factors predicting OS were analyzed using the Cox proportional hazard model. Risk stratification for overall survival was determined based on the results of multivariate analysis.
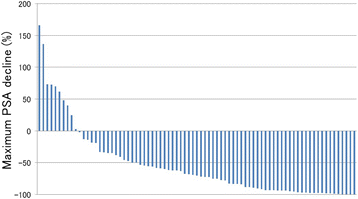
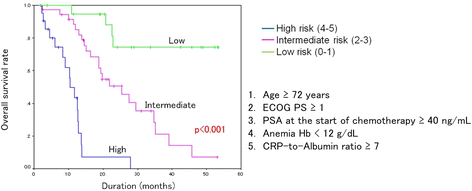
Results: PSA response ≥50 % was observed in 55 (69.6 %) of all patients, and the median OS was 22.5 months. The multivariate analysis showed that age, serum PSA level at the start of chemotherapy, and Hb were independent prognostic factors for OS. In addition, ECOG performance status (PS) and the CRP-to-albumin ratio were not significant but were considered possible predictors for OS. Risk stratification according to the number of these risk factors could effectively stratify CRPC patients treated with docetaxel in terms of OS.
Conclusions: Age, serum PSA level at the start of chemotherapy, and Hb were identified as independent prognostic factors of OS. ECOG PS and the CRP-to-albumin ratio were not significant, but were considered possible predictors for OS in Japanese CRPC patients treated with docetaxel. Risk stratification based on these factors could be helpful for estimating overall survival.
Keywords: Castration-resistant prostate cancer; Docetaxel; Prognostic factor.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous