Clinical outcomes of EGFR-TKI treatment and genetic heterogeneity in lung adenocarcinoma patients with EGFR mutations on exons 19 and 21
- PMID: 27001083
- PMCID: PMC4802875
- DOI: 10.1186/s40880-016-0086-2
Clinical outcomes of EGFR-TKI treatment and genetic heterogeneity in lung adenocarcinoma patients with EGFR mutations on exons 19 and 21
Abstract
Background: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations, including a known exon 19 deletion (19 del) and exon 21 L858R point mutation (L858R mutation), are strong predictors of the response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) treatment in lung adenocarcinoma. However, whether patients carrying EGFR 19 del and L858R mutations exhibit different responsiveness to EGFR-TKIs and what are the potential mechanism for this difference remain controversial. This study aimed to investigate the clinical outcomes of EGFR-TKI treatment in patients with EGFR 19 del and L858R mutations and explore the genetic heterogeneity of tumors with the two mutation subtypes.
Methods: Of 1127 patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR 19 del or L858R mutations, 532 received EGFR-TKI treatment and were included in this study. EGFR 19 del and L858R mutations were detected by using denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC). T790M mutation, which is a common resistant mutation on exon 20 of EGFR, was detected by amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS). Next-generation sequencing (NGS) was used to explore the genetic heterogeneity of tumors with EGFR 19 del and L858R mutations.
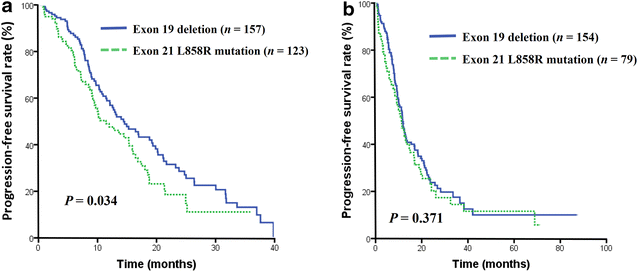
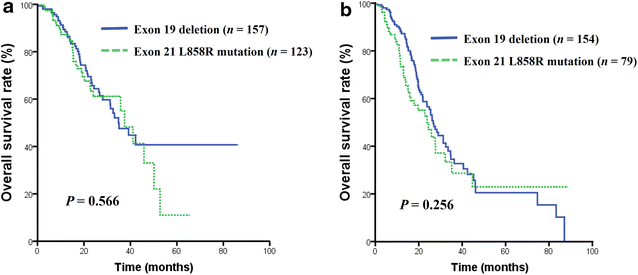
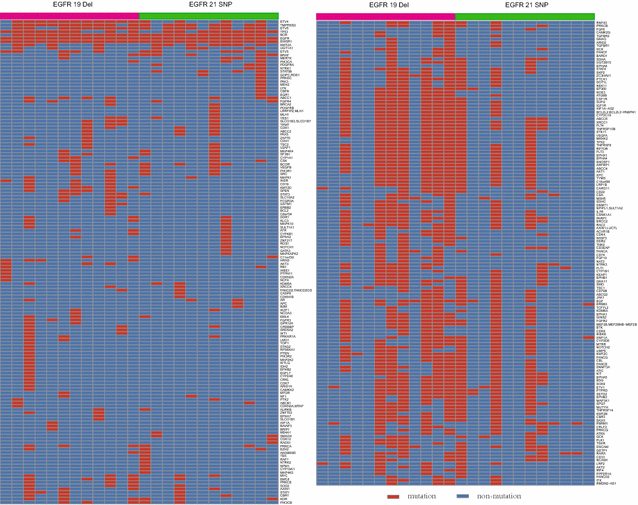
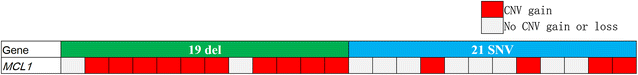
Results: Of the 532 patients, 319 (60.0%) had EGFR 19 del, and 213 (40.0%) had L858R mutations. The patients with EGFR 19 del presented a significantly higher overall response rate (ORR) for EGFR-TKI treatment (55.2% vs. 43.7%, P = 0.017) and had a longer progression-free survival (PFS) after first-line EGFR-TKI treatment (14.4 vs. 11.4 months, P = 0.034) compared with those with L858R mutations. However, no statistically significant difference in overall survival (OS) was observed between the two groups of patients. T790M mutation status was analyzed in 88 patients before EGFR-TKI treatment and 134 after EGFR-TKI treatment, and there was no significant difference in the co-existence of T790M mutation with EGFR 19 del and L858R mutations before EGFR-TKI treatment (5.6% vs. 8.8%, P = 0.554) or after treatment (24.4% vs. 35.4%, P = 0.176). In addition, 24 patients with EGFR 19 del and 19 with L858R mutations were analyzed by NGS, and no significant difference in the presence of multiple somatic mutations was observed between the two genotypes.
Conclusions: Patients with EGFR 19 del exhibit longer PFS and higher ORR compared with those with L858R mutations. Whether the heterogeneity of tumors with EGFR 19 del and L858R mutations contribute to a therapeutic response difference needs further investigation.
Keywords: EGFR exon 19 deletion; EGFR exon 21 L858R point mutation; Lung adenocarcinoma; Treatment efficacy.
Figures
References
-
- Fukuoka M, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Sunpaweravong P, Leong SS, Sriuranpong V, et al. Biomarker analyses and final overall survival results from a phase III, randomized, open-label, first-line study of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer in Asia (IPASS) J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(21):2866–2874. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.33.4235. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gao G, Ren S, Li A, Xu J, Xu Q, Su C, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy is effective as first-line treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR: a meta-analysis from six phase III randomized controlled trials. Int J Cancer. 2012;131(5):E822–E829. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27396. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Carey KD, Garton AJ, Romero MS, Kahler J, Thomson S, Ross S, et al. Kinetic analysis of epidermal growth factor receptor somatic mutant proteins shows increased sensitivity to the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, erlotinib. Cancer Res. 2006;66(16):8163–8171. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0453. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

