Effects of a New Emollient-Based Treatment on Skin Microflora Balance and Barrier Function in Children with Mild Atopic Dermatitis
- PMID: 27001317
- PMCID: PMC5071726
- DOI: 10.1111/pde.12786
Effects of a New Emollient-Based Treatment on Skin Microflora Balance and Barrier Function in Children with Mild Atopic Dermatitis
Abstract
Background/objectives: The use of emollients is widely recommended for the management of atopic dermatitis (AD), especially between flares. An imbalance of skin microflora is suspected of playing a key role in exacerbations of AD. Our aim was to evaluate the effect of a new emollient balm on clinical parameters (SCORing Atopic Dermatitis [SCORAD], xerosis, pruritus), skin barrier function (transepidermal water loss and loricrin, filaggrin, corneodesmosin, and involucrin expression], skin microflora biodiversity, and Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis balance in children with mild AD.
Methods: Fifty-four children (1-4 yrs old) were enrolled in this randomized, controlled study. Subjects applied a hygiene product and the emollient balm (emollient group, n = 28) or the hygiene product only (control group, n = 26) twice a day for 28 days.
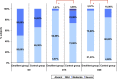
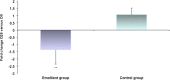
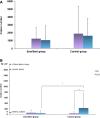
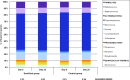
Results: We found improvement in favor of the emollient group in SCORAD (p < 0.001), pruritus (p = 0.06), and xerosis (p = 0.06) after 28 days of application. Moreover, transepidermal water loss decreased in the emollient group by 34% (p = 0.06) and involucrin expression by 37% (p = 0.001) at day 28 from baseline in association with improvement in barrier function, whereas other barrier-specific proteins did not vary. S. aureus increased significantly in the control group only (6.5 times, p = 0.01), whereas S. epidermidis remained stable in both groups. The Shannon index (H' = 2.3) did not vary with treatment in either group.
Conclusion: Twice-daily application of a new emollient balm in children with mild AD protected the skin from S. aureus proliferation and preserved microflora biodiversity.
© 2016 Pierre Fabre Dermo-Cosmétique. Pediatric Dermatology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Cork MJ, Danby SG, Vasilopoulos Y et al. Epidermal barrier dysfunction in atopic dermatitis. J Invest Dermatol 2009;129:1892–1908. - PubMed
-
- Zollner TM, Wichelhaus TA, Hartung A et al. Colonization with superantigen‐producing Staphylococcus aureus is associated with increased severity of atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Allergy 2000;30:994–1000. - PubMed
-
- Casas C, Ginisty H, Alvarez‐Georges S et al. Molecular characterization of inflammation and Staphylococcus aureus colonization of involved skin of atopic dermatitis patients. A non‐invasive approach. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 2008;21:260–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

