Hepatitis B Vaccination Coverage and Prevalence of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Among Children in French Polynesia, 2014
- PMID: 27001757
- PMCID: PMC4889759
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.15-0903
Hepatitis B Vaccination Coverage and Prevalence of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Among Children in French Polynesia, 2014
Abstract
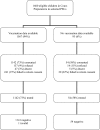
French Polynesia is considered to be moderately endemic for chronic hepatitis B virus infection, with an estimated 3% of the population having hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg). From 1990 to 1992, a 3-dose hepatitis B vaccination series was introduced into the routine infant immunization schedule in French Polynesia, including a birth dose (BD). In 2014, a nationally representative 2-stage cluster survey was undertaken to evaluate the impact of the vaccination program on HBsAg prevalence among school children (∼6 years of age) in Cours Préparatoire (CP). Documented vaccination data were reviewed for all eligible children; children with consent were tested for HBsAg with a rapid point-of-care test. In total, 1,660 students were identified; 1,567 (94%) had vaccination data for review and 1,196 (72%) participated in the serosurvey. Three-dose vaccination coverage was 98%, while timely BD coverage, defined as a dose administered within 24 hours of life, was 89%. Receipt of the second and third doses was often delayed, with 75% and 55% receiving a second and third dose within 1 month of the recommended age, respectively. No children tested positive for HBsAg. French Polynesia's vaccination program has achieved high coverage and an HBsAg seroprevalence of 0% (0-0.5%) among CP school children, but timeliness of vaccination could be improved.
© The American Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Low Level of Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Children 20 Years After Initiation of Infant Vaccination Program in Wallis and Futuna.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017 Mar;96(3):715-719. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.16-0596. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2017. PMID: 28070010 Free PMC article.
-
[Control of hepatitis B in French Polynesia with a program of systematic vaccination of newborns with the Genhevac B vaccine].Sante. 1996 Jan-Feb;6(1):11-5. Sante. 1996. PMID: 8612008 French.
-
Nationwide representative serosurvey of third-grade school children to evaluate the hepatitis B vaccination impact in Kyrgyzstan, 2022.BMC Infect Dis. 2025 Jan 22;25(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-10491-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39844081 Free PMC article.
-
Mass vaccination against hepatitis B: the French example.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006;304:115-29. doi: 10.1007/3-540-36583-4_7. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16989267 Review.
-
Implications of Birth-Dose Vaccination against Hepatitis B Virus in Southeast Asia.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Apr 12;9(4):374. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9040374. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33921259 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis B vaccine development and implementation.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020 Jul 2;16(7):1533-1544. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1732166. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020. PMID: 32186974 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the determinants of human health in French Polynesia: the MATAEA project.Front Epidemiol. 2023 Nov 27;3:1201038. doi: 10.3389/fepid.2023.1201038. eCollection 2023. Front Epidemiol. 2023. PMID: 38455935 Free PMC article.
-
Towards elimination of chronic viral hepatitis in French Polynesia: results from a national population-based survey.Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2024 Mar 2;45:101035. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2024.101035. eCollection 2024 Apr. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2024. PMID: 38445260 Free PMC article.
-
Timeliness of routine childhood vaccination in 103 low-and middle-income countries, 1978-2021: A scoping review to map measurement and methodological gaps.PLOS Glob Public Health. 2022 Jul 14;2(7):e0000325. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0000325. eCollection 2022. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36962319 Free PMC article.
-
Progress towards triple elimination of mother-to-child transmission of HIV, hepatitis B and syphilis in Pacific Island Countries and Territories: a systematic review.Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2023 Apr 5;35:100740. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100740. eCollection 2023 Jun. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2023. PMID: 37424691 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ott JJ, Stevens GA, Groeger J, Wiersma ST. Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection: new estimates of age-specific HBsAg seroprevalence and endemicity. Vaccine. 2012;30:2212–2219. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein ST, Zhou F, Hadler SC, Bell BP, Mast EE, Margolis HS. A mathematical model to estimate global hepatitis B disease burden and vaccination impact. Int J Epidemiol. 2005;34:1329–1339. - PubMed
-
- Clements CJ, Baoping Y, Crouch A, Hipgrave D, Mansoor O, Nelson CB, Treleaven S, van Konkelenberg R, Wiersma S. Progress in the control of hepatitis B infection in the Western Pacific Region. Vaccine. 2006;24:1975–1982. - PubMed
-
- Hennessey K, Mendoza-Aldana J, Bayutas B, Lorenzo-Mariano KM, Diorditsa S. Hepatitis B control in the World Health Organization's Western Pacific Region: targets, strategies, status. Vaccine. 2013;31(Suppl 9):J85–J92. - PubMed
-
- Regional Committee of the Western Pacific . Manila, Philippines: WHO Regional Office for the Western Pacific; 2013. Hepatitis B Control through Vaccination: Setting the Target. WPR/RC64.R5.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

