Clinical progression of ocular injury following arsenical vesicant lewisite exposure
- PMID: 27002633
- PMCID: PMC5082841
- DOI: 10.3109/15569527.2015.1127255
Clinical progression of ocular injury following arsenical vesicant lewisite exposure
Abstract
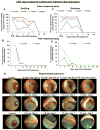
Ocular injury by lewisite (LEW), a potential chemical warfare and terrorist agent, results in edema of eyelids, inflammation, massive corneal necrosis and blindness. To enable screening of effective therapeutics to treat ocular injury from LEW, useful clinically-relevant endpoints are essential. Hence, we designed an efficient exposure system capable of exposing up to six New-Zealand white rabbits at one time, and assessed LEW vapor-induced progression of clinical ocular lesions mainly in the cornea. The right eye of each rabbit was exposed to LEW (0.2 mg/L) vapor for 2.5, 5.0, 7.5 and 10.0 min and clinical progression of injury was observed for 28 days post-exposure (dose-response study), or exposed to same LEW dose for 2.5 and 7.5 min and clinical progression of injury was observed for up to 56 days post-exposure (time-response study); left eye served as an unexposed control. Increasing LEW exposure caused corneal opacity within 6 h post-exposure, which increased up to 3 days, slightly reduced thereafter till 3 weeks, and again increased thereafter. LEW-induced corneal ulceration peaked at 1 day post-exposure and its increase thereafter was observed in phases. LEW exposure induced neovascularization starting at 7 days which peaked at 22-35 days post-exposure, and remained persistent thereafter. In addition, LEW exposure caused corneal thickness, iris redness, and redness and swelling of the conjunctiva. Together, these findings provide clinical sequelae of ocular injury following LEW exposure and for the first time establish clinically-relevant quantitative endpoints, to enable the further identification of histopathological and molecular events involved in LEW-induced ocular injury.
Keywords: Iris redness; Lewisite; clinical lesions; conjunctival injury; corneal opacity; corneal thickness; corneal ulceration; efficient exposure system; neovascularization.
Figures







References
-
- Lindsay CD, Hambrook JL, Brown RF, Platt JC, Knight R, Rice P. Examination of changes in connective tissue macromolecular components of large white pig skin following application of Lewisite vapour. Journal of applied toxicology : JAT. 2004;24(1):37–46. - PubMed
-
- Sahu C, Pakhira S, Sen K, Das AK. A computational study of detoxification of lewisite warfare agents by British anti-lewisite: catalytic effects of water and ammonia on reaction mechanism and kinetics. The journal of physical chemistry A. 2013;117(16):3496–506. Epub 2013/04/02. - PubMed
-
- Kehe K, Flohe S, Krebs G, Kreppel H, Reichl FX, Liebl B, et al. Effects of Lewisite on cell membrane integrity and energy metabolism in human keratinocytes and SCL II cells. Toxicology. 2001;163(2-3):137–44. Epub 2001/08/23. - PubMed
-
- King JR, Riviere JE, Monteiro-Riviere NA. Characterization of lewisite toxicity in isolated perfused skin. Toxicology and applied pharmacology. 1992;116(2):189–201. Epub 1992/10/01. - PubMed
-
- Nelson P, Hancock JR, Sawyer TW. Therapeutic effects of hypothermia on Lewisite toxicity. Toxicology. 2006;222(1-2):8–16. Epub 2006/02/21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
