The effect of nanoparticle size on in vivo pharmacokinetics and cellular interaction
- PMID: 27003448
- PMCID: PMC5561790
- DOI: 10.2217/nnm.16.5
The effect of nanoparticle size on in vivo pharmacokinetics and cellular interaction
Abstract
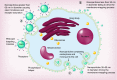
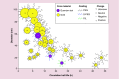
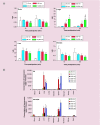
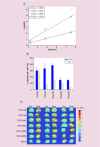
Nanoparticle-based technologies offer exciting new approaches to disease diagnostics and therapeutics. To take advantage of unique properties of nanoscale materials and structures, the size, shape and/or surface chemistry of nanoparticles need to be optimized, allowing their functionalities to be tailored for different biomedical applications. Here we review the effects of nanoparticle size on cellular interaction and in vivo pharmacokinetics, including cellular uptake, biodistribution and circulation half-life of nanoparticles. Important features of nanoparticle probes for molecular imaging and modeling of nanoparticle size effects are also discussed.
Keywords: cellular uptake; in vivo pharmacokinetics; modeling; nanoparticle; size effect.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute of the NIH as a Program of Excellence in Nanotechnology award (HHSN268201000043C to GB). The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Albanese A, Tang PS, Chan WCW. The effect of nanoparticle size, shape, and surface chemistry on biological systems. Ann. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012;14:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Kulkarni SA, Feng SS. Effects of particle size and surface modification on cellular uptake and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery. Pharmaceut. Res. 2013;30:2512–2522. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
