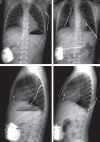
Subcutaneous defibrillator implantation in pediatric patients
- PMID: 27004712
- PMCID: PMC5368523
- DOI: 10.5152/AnatolJCardiol.2015.6589
Subcutaneous defibrillator implantation in pediatric patients
Abstract
Objective: Although sudden cardiac death is rare in children, an intracardiac defibrillator system is indicated in children with various types of cardiomyopathy, primary electrical diseases, and after surgical repair of congenital heart defects. The use of transvenous defibrillator lead systems is limited in pediatric patients because of a small body size and/or limited vascular access. Subcutaneous array leads combined with an abdominally placed generator can enable implantation.
Method: This is a retrospective study of 13 patients who underwent subcutaneous defibrillator implantation between September 2010 and March 2015. The subcutaneous system was preferred because patients were not amenable to transvenous lead placement.
Results: The median patient age was 4.1 years, and the median patient weight was 12.1 kg. Diagnoses of patients were long-QT syndrome in 6, aborted cardiac arrest with left ventricular non-compaction in 3, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with sustained ventricular tachycardia in 3, and arrythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy in 1. Revision of the subcutaneous lead was required in 5 patients 2-26 months after the implantation. Appropriate shocks were observed in three patients. Inappropriate shock and lead fractures were observed in one patient during the follow-up period. The failure of therapy was observed in one patient. There were no perioperative complications and no early or late deaths.
Conclusion: Subcutaneous defibrillator systems are safe and effective in pediatric patients when the transvenous method is risky and contraindicated. Because the high growth rate in this population leads to lead failures, a close follow-up of this population is essential.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
A multicenter experience with novel implantable cardioverter defibrillator configurations in the pediatric and congenital heart disease population.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2006 Jan;17(1):41-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2005.00271.x. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2006. PMID: 16426398
-
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy in paediatric practice: a single-centre UK experience with focus on subcutaneous defibrillation.Europace. 2013 Apr;15(4):523-30. doi: 10.1093/europace/eus388. Epub 2013 Jan 20. Europace. 2013. PMID: 23333943
-
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator implantation in children in The Netherlands.Eur J Pediatr. 2005 Jul;164(7):436-41. doi: 10.1007/s00431-005-1668-1. Epub 2005 Apr 21. Eur J Pediatr. 2005. PMID: 15843980
-
[Transvenous subcutaneous implantation technique of the cardioverter/defibrillator].Herz. 1994 Oct;19(5):259-77. Herz. 1994. PMID: 8001899 Review. German.
-
Efficacy and Complications of Subcutaneous versus Conventional Cardioverter Defibrillators: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2022;18(3):e081221198647. doi: 10.2174/1573403X17666211208100151. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 34879809 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clinical outcomes of implantable cardioverter-defibrillator therapy in noncompaction cardiomyopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Heart Fail Rev. 2023 Jan;28(1):241-248. doi: 10.1007/s10741-022-10250-w. Epub 2022 Jun 10. Heart Fail Rev. 2023. PMID: 35689132 Free PMC article.
-
Brazilian Guidelines for Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices - 2023.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2023 Jan 23;120(1):e20220892. doi: 10.36660/abc.20220892. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36700596 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese. No abstract available.
References
-
- Liberthson RR. Sudden death from cardiac causes in children and young adults. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:1039–44. - PubMed
-
- Silka MJ, Kron J, Dunnigan A, Dick M., 2nd Sudden cardiac death and the use of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators in pediatric patients. The Pediatric Electrophysiology Society. Circulation. 1993;87:800–7. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Cohen Y, Berul CI, Alexander ME, Fortescue EB, Walsh EP, Triedman JK, et al. Age, size, and lead factors alone do not predict venous obstruction in children and young adults with transvenous lead systems. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2006;17:754–9. - PubMed
-
- Luedemann M, Hund K, Stertmann W, Michel-Behnke I, Gonzales M, Akintuerk H, et al. Implantable cardioverter defibrillator in a child using a single subcutaneous array lead and an abdominal active can. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2004;27:117–9. - PubMed
-
- Griksaitis MJ, Rosengarten JA, Gnanapragasam JP, Haw MP, Morgan JM. Implantable cardioverter defibrillator therapy in paediatric practice:a single-centre UK experience with focus on subcutaneous defibrillation. Europace. 2013;15:523–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources