Development of Photoactivated Fluorescent N-Hydroxyoxindoles and Their Application for Cell-Selective Imaging
- PMID: 27004772
- PMCID: PMC5808866
- DOI: 10.1002/chem.201600547
Development of Photoactivated Fluorescent N-Hydroxyoxindoles and Their Application for Cell-Selective Imaging
Abstract
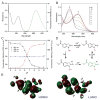
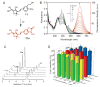
Photoactivatable fluorophores are essential tools for studying the dynamic molecular interactions within important biological systems with high spatiotemporal resolution. However, currently developed photoactivatable fluorophores based on conventional dyes have several limitations including reduced photoactivation efficiency, cytotoxicity, large molecular size, and complicated organic synthesis. To overcome these challenges, we herein report a class of photoactivatable fluorescent N-hydroxyoxindoles formed through the intramolecular photocyclization of substituted o-nitrophenyl ethanol (ONPE). These oxindole fluorophores afford excellent photoactivation efficiency with ultra-high fluorescence enhancement (up to 800-fold) and are small in size. Furthermore, the oxindole derivatives show exceptional biocompatibility by generating water as the only photolytic side product. Moreover, structure-activity relationship analysis clearly revealed the strong correlation between the fluorescent properties and the substituent groups, which can serve as a guideline for the further development of ONPE-based fluorescent probes with desired photophysical and biological properties. As a proof-of-concept, we demonstrated the capability of a new substituted ONPE that has an uncaging wavelength of 365-405 nm and an excitation/emission at 515 and 620 nm, for the selective imaging of a cancer cell line (Hela cells) and a human neural stem cell line (hNSCs).
Keywords: cage compounds; dyes/pigments; fluorescence imaging; fluorescent probes; oxindole.
© 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures



Similar articles
-
New caged coumarin fluorophores with extraordinary uncaging cross sections suitable for biological imaging applications.J Am Chem Soc. 2004 Apr 14;126(14):4653-63. doi: 10.1021/ja036958m. J Am Chem Soc. 2004. PMID: 15070382
-
Development of a Photoactivatable Phosphine Probe for Induction of Intracellular Reductive Stress with Single-Cell Precision.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2016 Nov 14;55(47):14709-14712. doi: 10.1002/anie.201608779. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2016. PMID: 27763731
-
Rapid, photoactivatable turn-on fluorescent probes based on an intramolecular photoclick reaction.J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Aug 10;133(31):11912-5. doi: 10.1021/ja204758c. Epub 2011 Jul 15. J Am Chem Soc. 2011. PMID: 21736329 Free PMC article.
-
Photoactivatable fluorophores and techniques for biological imaging applications.Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2012 Mar;11(3):460-71. doi: 10.1039/c2pp05342j. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22252510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photoactivatable BODIPYs for Live-Cell PALM.Molecules. 2023 Mar 7;28(6):2447. doi: 10.3390/molecules28062447. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36985424 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A light-activated magnetic bead strategy utilized in spatio-temporal controllable exosomes isolation.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Sep 6;10:1006374. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1006374. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36147530 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed Degradation of Hydrogels with a Double-Locked Domain.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019 Feb 25;58(9):2820-2825. doi: 10.1002/anie.201811848. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2019. PMID: 30569555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- FernQndez-Su Qrez M, Ting AY. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

