The role of neutrophils in immune dysfunction during severe inflammation
- PMID: 27005275
- PMCID: PMC4804478
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-016-1250-4
The role of neutrophils in immune dysfunction during severe inflammation
Abstract
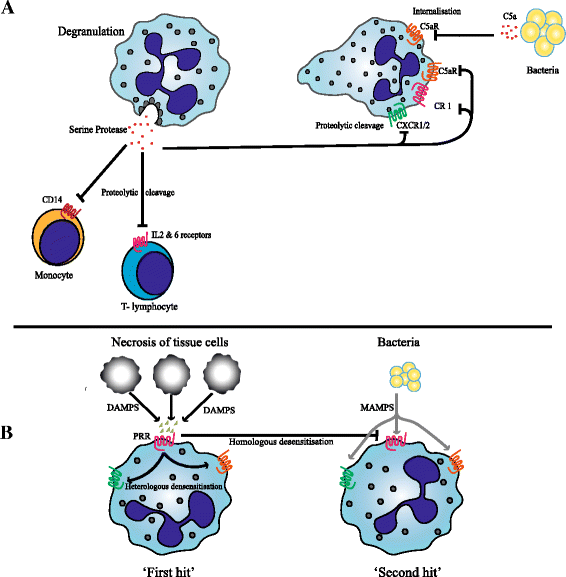
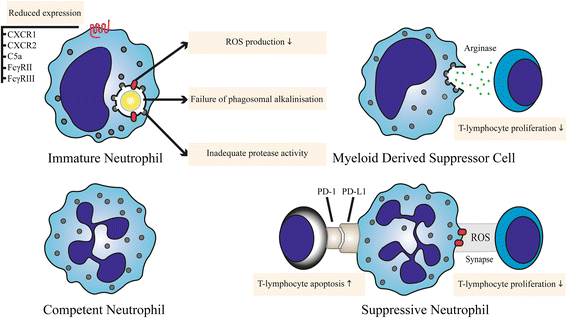
Critically ill post-surgical, post-trauma and/or septic patients are characterised by severe inflammation. This immune response consists of both a pro- and an anti-inflammatory component. The pro-inflammatory component contributes to (multiple) organ failure whereas occurrence of immune paralysis predisposes to infections. Strikingly, infectious complications arise in these patients despite the presence of a clear neutrophilia. We propose that dysfunction of neutrophils potentially increases the susceptibility to infections or can result in the inability to clear existing infections. Under homeostatic conditions these effector cells of the innate immune system circulate in a quiescent state and serve as the first line of defence against invading pathogens. In severe inflammation, however, neutrophils are rapidly activated, which affects their functional capacities, such as chemotaxis, phagocytosis, intra-cellular killing, NETosis, and their capacity to modulate adaptive immunity. This review provides an overview of the current understanding of neutrophil dysfunction in severe inflammation. We will discuss the possible mechanisms of downregulation of anti-microbial function, suppression of adaptive immunity by neutrophils and the contribution of neutrophil subsets to immune paralysis.
Figures
Comment in
-
Measurement of functional and morphodynamic neutrophil phenotypes in systemic inflammation and sepsis.Crit Care. 2016 Aug 24;20(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1391-5. Crit Care. 2016. PMID: 27552803 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Neutrophil Activation During Septic Shock.Shock. 2018 Apr;49(4):371-384. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000980. Shock. 2018. PMID: 28858142 Review.
-
Plasticity of neutrophils reveals modulatory capacity.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2015 Aug;48(8):665-75. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20154524. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2015. PMID: 26108096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophils: Cinderella of innate immune system.Int Immunopharmacol. 2010 Nov;10(11):1325-34. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2010.08.012. Epub 2010 Sep 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20828640 Review.
-
The impact of trauma on neutrophil function.Injury. 2014 Dec;45(12):1824-33. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2014.06.021. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Injury. 2014. PMID: 25106876 Review.
-
Immunologic alterations and the pathogenesis of organ failure in the ICU.Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Oct;32(5):569-80. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1287865. Epub 2011 Oct 11. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2011. PMID: 21989693 Review.
Cited by
-
Managing Cancer Drug Resistance from the Perspective of Inflammation.J Oncol. 2022 Sep 19;2022:3426407. doi: 10.1155/2022/3426407. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36245983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An aging-related immune landscape in the hematopoietic immune system.Immun Ageing. 2024 Jan 2;21(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12979-023-00403-2. Immun Ageing. 2024. PMID: 38169405 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil heterogeneity and fate in inflamed tissues: implications for the resolution of inflammation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Sep 1;319(3):C510-C532. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00181.2020. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32667864 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Tumor Microenvironment and Treatment Strategies in Colorectal Cancer.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 2;12:792691. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.792691. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34925375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delta neutrophil index and shock index can stratify risk for the requirement for massive transfusion in patients with primary postpartum hemorrhage in the emergency department.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 15;16(10):e0258619. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258619. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34653202 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

