A scoping review of studies comparing the medication event monitoring system (MEMS) with alternative methods for measuring medication adherence
- PMID: 27005306
- PMCID: PMC4917812
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.12942
A scoping review of studies comparing the medication event monitoring system (MEMS) with alternative methods for measuring medication adherence
Abstract
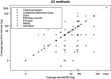
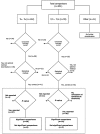
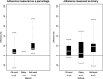
Different methods are available for measuring medication adherence. In this paper, we conducted a scoping review to identify and summarize evidence of all studies comparing the Medication Event Monitoring System (MEMS) with alternative methods for measuring medication adherence. A literature search was performed using the open database www.iAdherence.org that includes all original studies reporting findings from the MEMS. Papers comparing methods for measuring adherence to solid oral formulations were included. Data was extracted using a standardized extraction table. A total of 117 articles fulfilled the inclusion criteria, including 251 comparisons. Most frequent comparisons were against self-report (n = 119) and pill count (n = 59). Similar outcome measures were used in 210 comparisons (84%), among which 78 used dichotomous variables (adherent or not) and 132 used continuous measures (adherence expressed as percentage). Furthermore, 32% of all comparisons did not estimate adherence over the same coverage period and 44% of all comparisons did not use a statistical method or used a suboptimal one. Only eighty-seven (35%) comparisons had similar coverage periods, similar outcome measures and optimal statistical methods. Compared to MEMS, median adherence was grossly overestimated by 17% using self-report, by 8% using pill count and by 6% using rating. In conclusion, among all comparisons of MEMS versus alternative methods for measuring adherence, only a few used adequate comparisons in terms of outcome measures, coverage periods and statistical method. Researchers should therefore use stronger methodological frameworks when comparing measurement methods and be aware that non-electronic measures could lead to overestimation of medication adherence.
Keywords: measurement methods; medication adherence; medication event monitoring system; methodology; pill count; self-report.
© 2016 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Blaschke TF, Osterberg L, Vrijens B, Urquhart J. Adherence to medications: insights arising from studies on the unreliable link between prescribed and actual drug dosing histories. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2012; 52: 275–301. - PubMed
-
- Vrijens B, Urquhart J. Methods for measuring, enhancing, and accounting for medication adherence in clinical trials. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2014; 95: 617–26. - PubMed
-
- Demonceau J, Ruppar T, Kristanto P, Hughes DA, Fargher E, Kardas P, et al. Identification and assessment of adherence‐enhancing interventions in studies assessing medication adherence through electronically compiled drug dosing histories: a systematic literature review and meta‐analysis. Drugs 2013; 73: 545–62. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheng CW, Woo KS, Chan JC, Tomlinson B, You JH. Assessing adherence to statin therapy using patient report, pill count, and an electronic monitoring device. Am J Health Syst Pharm 2005; 62: 411–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

