CB1 antagonism produces behaviors more consistent with satiety than reduced reward value in food-maintained responding in rats
- PMID: 27005309
- PMCID: PMC5531753
- DOI: 10.1177/0269881116639287
CB1 antagonism produces behaviors more consistent with satiety than reduced reward value in food-maintained responding in rats
Abstract
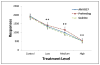
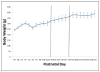
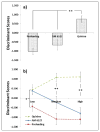
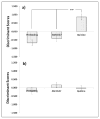
Cannabinoid CB1 antagonists are widely known to reduce motivation for food, but it is not known whether they induce satiety or reduce reward value of food. It may therefore be necessary to compare effects of altered satiety and reward food value in the same appetitive task, and determine whether CB1 antagonism produces a behavior pattern similar to either, both, or neither. A fine-grained analysis of fixed-ratio 10 (FR10) responding for palatable food initially included number and duration of, and between, all lever presses and food tray entries in order to differentiate the pattern of suppression of prefeeding from that caused by reducing the reward value of the pellets with quinine. Discriminant function analysis then determined that these manipulations were best differentiated by effects on tray entries, pellet retrieval latencies, and time of the first response. At 0.5 mg/kg, AM 6527 produced similar effects to reducing reward value, but at 1.0 and 4.0 mg/kg, effects were more similar to those when animals were satiated. We conclude that AM 6527 both reduced reward value and enhanced satiety, but as dose increased, effects on satiety became much more prominent. These findings contribute to knowledge about the behavioral processes affected by CB1 antagonism.
Keywords: Cannabinoid; motivation; multivariate analysis; obesity; reward.
© The Author(s) 2016.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Ameloot K, Janssen P, Scarpellini E, et al. Endocannabinoid control of gastric sensorimotor function in man. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;31:1123–1131. - PubMed
-
- Bellocchio L, Lafenetre P, Cannich A, et al. Bimodal control of stimulated food intake by the endocannabinoid system. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13:281–283. - PubMed
-
- Brown RM, Seiden LS. Inter-response time changes as a function of water deprivation and amphetamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975;193:701–712. - PubMed
-
- Cardinal P, Bellocchio L, Clark S, et al. Hypothalamic CB1 cannabinoid receptors regulate energy balance in mice. Endocrinology. 2012;153:4136–4143. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

