Biodegradation of Phenol by Bacteria Strain Acinetobacter Calcoaceticus PA Isolated from Phenolic Wastewater
- PMID: 27005648
- PMCID: PMC4808963
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph13030300
Biodegradation of Phenol by Bacteria Strain Acinetobacter Calcoaceticus PA Isolated from Phenolic Wastewater
Abstract
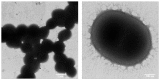
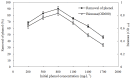
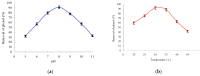
A phenol-degrading bacterium strain PA was successfully isolated from the effluent of petrochemical wastewater. Based on its morphological, physiological and biochemical characteristics, the strain PA was characterized as a Gram-negative, strictly aerobic, nonmotile and short rod-shaped bacterium that utilizes phenol as a sole carbon and energy source. 16S rDNA sequence analysis revealed that this strain is affiliated to Acinetobacter calcoaceticus in the group of Gammaproteobacteria. The strain was efficient in removing 91.6% of the initial 800 mg ∙ L(-1) phenol within 48 h, and had a tolerance of phenol concentration as high as 1700 mg ∙ L(-1). These results indicated that A. calcoaceticus possesses a promising potential in treating phenolic wastewater.
Keywords: Acinetobacter calcoaceticus; biodegradation; phenol-degrading.
Figures

References
-
- Arutchelvan V., Kanakasabai V., Nagarajan S., Muralikrishnan V. Isolation and identification of novel high strength phenol degrading bacterial strains from phenol-formaldehyde resin manufacturing industrial wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005;127:238–243. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.04.043. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hooived M., Heederik D.J.J., Kogevinas M., Boffetta P., Needham L.L., Patterson D.G., Bueno-de-Mesquita H.B. Second follow-up of a dutch cohort occupationally exposed to phenoxy herbicides, chlorophenols, and contaminants. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1998;147:891–899. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a009543. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Sampling and Analysis Procedure for Screening of Industrial Effluents for Priority Pollutants. EPA; Cincinnati, OH, USA: 1977.
-
- Lin S.H., Chuang T.S. Combined treatment of phenolic wastewater by wet air oxidation and activated sludge. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 1994;44:243–258. doi: 10.1080/02772249409358063. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

