Molecular Mechanisms of HTLV-1 Cell-to-Cell Transmission
- PMID: 27005656
- PMCID: PMC4810264
- DOI: 10.3390/v8030074
Molecular Mechanisms of HTLV-1 Cell-to-Cell Transmission
Abstract
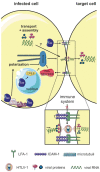
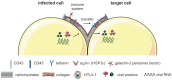
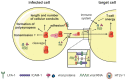
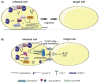
The tumorvirus human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1), a member of the delta-retrovirus family, is transmitted via cell-containing body fluids such as blood products, semen, and breast milk. In vivo, HTLV-1 preferentially infects CD4⁺ T-cells, and to a lesser extent, CD8⁺ T-cells, dendritic cells, and monocytes. Efficient infection of CD4⁺ T-cells requires cell-cell contacts while cell-free virus transmission is inefficient. Two types of cell-cell contacts have been described to be critical for HTLV-1 transmission, tight junctions and cellular conduits. Further, two non-exclusive mechanisms of virus transmission at cell-cell contacts have been proposed: (1) polarized budding of HTLV-1 into synaptic clefts; and (2) cell surface transfer of viral biofilms at virological synapses. In contrast to CD4⁺ T-cells, dendritic cells can be infected cell-free and, to a greater extent, via viral biofilms in vitro. Cell-to-cell transmission of HTLV-1 requires a coordinated action of steps in the virus infectious cycle with events in the cell-cell adhesion process; therefore, virus propagation from cell-to-cell depends on specific interactions between cellular and viral proteins. Here, we review the molecular mechanisms of HTLV-1 transmission with a focus on the HTLV-1-encoded proteins Tax and p8, their impact on host cell factors mediating cell-cell contacts, cytoskeletal remodeling, and thus, virus propagation.
Keywords: HTLV-1; Tax; cell-cell contacts; cell-to-cell transmission; cellular conduit; p8; viral biofilm; virological synapse; virus transmission.
Figures

References
-
- Poiesz B.J., Ruscetti F.W., Gazdar A.F., Bunn P.A., Minna J.D., Gallo R.C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1980;77:7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7415. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yoshida M., Seiki M., Yamaguchi K., Takatsuki K. Monoclonal integration of human T-cell leukemia provirus in all primary tumors of adult T-cell leukemia suggests causative role of human T-cell leukemia virus in the disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1984;81:2534–2537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2534. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

