Antioxidant Capacities of Hot Water Extracts and Endopolysaccharides of Selected Chinese Medicinal Fruits
- PMID: 27005663
- PMCID: PMC4810117
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers8030033
Antioxidant Capacities of Hot Water Extracts and Endopolysaccharides of Selected Chinese Medicinal Fruits
Abstract
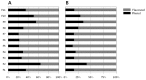
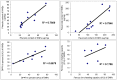
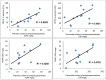
Fruits are a rich source of antioxidants and traditional Chinese fruits have been studied for their chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic properties against cancers and other diseases. The total phenol and flavonoid contents of eleven Chinese fruits extracts were determined. Total phenolic and flavonoid contents were estimated by both the Folin-Ciocalteau and aluminium chloride methods. The antioxidant activities were evaluated by four assays: a biological assay using Saccharomyces cerevisiae, DPPH radical scavenging activity, chelating ability for ferrous ions and ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP). The phenols and flavonoids contents of the hot water extracts were in the range of 17.7 to 94.7 mg/g and 12.3 to 295.4 mg/g, whereas the endopolysaccharides lie in the range of 4.5 to 77.4 mg/g and 22.7 to 230.0 mg/g. Significant amounts of phenols and flavonoids were present in the majority of the fruit extracts and showed strong antioxidant activities. The antioxidant properties of the fruit extracts of Crataegus pinnatifida, Illicium verum, Ligustrum lucidum, Momordica grosvenori and Psoralea corylifolia as determined by the DPPH and FRAP methods, were significant compared to other fruit extracts. In the present study, we found that significant amounts of phenolic and flavonoid compounds were present in these fruit extracts and may contribute to in vitro antioxidant activities.
Keywords: anti-oxidant activity; flavonoids; fruits; phenols; polysaccharides.
Figures



References
-
- Liu H., Visner G.A. Oxidants and antioxidants. In: Dani S.Z., Helmut H., Jaishree J., Abida K.H., Philip T.C., Roberto B., editors. Molecular Pathology of Lung Diseases. Volume 1. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2008. pp. 470–475. Molecular Pathology Library.
-
- Zhang L., Ravipati A.S., Koyyalamudi S.R., Jeong S.C., Reddy N., Smith P.T., Bartlett J., Shanmugam K., Münch D.G., Wu M.J. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of selected medicinal plants containing phenolic and flavonoid compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011;59:12361–12367. doi: 10.1021/jf203146e. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Diaz M.N., Frei B., Vita J.E., Keaney J.F. Antioxidants and atherosclerotic heart disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997;337:408–416. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

