Transient postoperative atrial fibrillation after abdominal aortic aneurysm repair increases mortality risk
- PMID: 27005752
- PMCID: PMC5110229
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvs.2015.12.046
Transient postoperative atrial fibrillation after abdominal aortic aneurysm repair increases mortality risk
Erratum in
-
Correction.J Vasc Surg. 2017 Jan;65(1):283. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2016.11.001. J Vasc Surg. 2017. PMID: 28010868 No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to determine whether new-onset transient postoperative atrial fibrillation (TPAF) affects mortality rates after abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) repair and to identify predictors for the development of TPAF.
Methods: Patients who underwent open aortic repair or endovascular aortic repair for a principal diagnosis AAA were retrospectively identified using the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project-State Inpatient Database (Florida) for 2007 to 2011 and monitored longitudinally for 1 year. Inpatient and 1-year mortality rates were compared between those with and without TPAF. TPAF was defined as new-onset atrial fibrillation that developed in the postoperative period and subsequently resolved in patients without a history of atrial fibrillation. Cox proportional hazards models, adjusted for age, gender, comorbidities, rupture status, and repair method, were used to assess 1-year survival. Predictive models were built with preoperative patient factors using Chi-squared Automatic Interaction Detector decision trees and externally validated on patients from California.
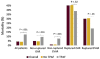
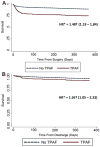
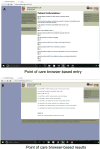
Results: A 3.7% incidence of TPAF was identified among 15,148 patients who underwent AAA repair. The overall mortality rate was 4.3%. The inpatient mortality rate was 12.3% in patients with TPAF vs 4.0% in those without TPAF. In the ruptured setting, the difference in mortality was similar between groups (33.7% vs 39.9%, P = .3). After controlling for age, gender, comorbid disease severity, urgency (ruptured vs nonruptured), and repair method, TPAF was associated with increased 1-year postoperative mortality (hazard ratio, 1.48; P < .001) and postdischarge mortality (hazard ratio, 1.56; P = .028). Chi-squared Automatic Interaction Detector-based models (C statistic = 0.70) were integrated into a Web-based application to predict an individual's probability of developing TPAF at the point of care.
Conclusions: The development of TPAF is associated with an increased risk of mortality in patients undergoing repair of nonruptured AAA. Predictive modeling can be used to identify those patients at highest risk for developing TPAF and guide interventions to improve outcomes.
Copyright © 2016 Society for Vascular Surgery. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Author conflict of interest: none.
Figures
References
-
- Wyse DG, Waldo AL, DiMarco JP, Domanski MJ, Rosenberg Y, Schron EB, et al. A comparison of rate control and rhythm control in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1825–33. - PubMed
-
- Wolf PA, Abbott RD, Kannel WB. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: the Framingham Study. Stroke. 1991;22:983–8. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin EJ, Wolf PA, D'Agostino RB, Silbershatz H, Kannel WB, Levy D. Impact of atrial fibrillation on the risk of death: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 1998;98:946–52. - PubMed
-
- Mathew JP, Parks R, Savino JS, Friedman AS, Koch C, Mangano DT, et al. Atrial fibrillation following coronary artery bypass graft surgery: predictors, outcomes, and resource utilization. MultiCenter Study of Perioperative Ischemia Research Group. JAMA. 1996;276:300–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

