A heme-binding domain controls regulation of ATP-dependent potassium channels
- PMID: 27006498
- PMCID: PMC4833257
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1600211113
A heme-binding domain controls regulation of ATP-dependent potassium channels
Abstract
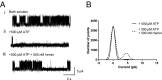
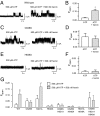
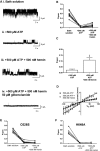
Heme iron has many and varied roles in biology. Most commonly it binds as a prosthetic group to proteins, and it has been widely supposed and amply demonstrated that subtle variations in the protein structure around the heme, including the heme ligands, are used to control the reactivity of the metal ion. However, the role of heme in biology now appears to also include a regulatory responsibility in the cell; this includes regulation of ion channel function. In this work, we show that cardiac KATP channels are regulated by heme. We identify a cytoplasmic heme-binding CXXHX16H motif on the sulphonylurea receptor subunit of the channel, and mutagenesis together with quantitative and spectroscopic analyses of heme-binding and single channel experiments identified Cys628 and His648 as important for heme binding. We discuss the wider implications of these findings and we use the information to present hypotheses for mechanisms of heme-dependent regulation across other ion channels.
Keywords: KATP channel; SUR2A; heme; heme regulation; potassium channel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Hou S, Reynolds MF, Horrigan FT, Heinemann SH, Hoshi T. Reversible binding of heme to proteins in cellular signal transduction. Acc Chem Res. 2006;39(12):918–924. - PubMed
-
- Rodgers KR. Heme-based sensors in biological systems. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1999;3(2):158–167. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu T. Binding of cysteine thiolate to the Fe(III) heme complex is critical for the function of heme sensor proteins. J Inorg Biochem. 2012;108:171–177. - PubMed
-
- Smith AG, Raven EL, Chernova T. The regulatory role of heme in neurons. Metallomics. 2011;3(10):955–962. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu T, et al. Gaseous O2, NO, and CO in signal transduction: Structure and function relationships of heme-based gas sensors and heme-redox sensors. Chem Rev. 2015;115(13):6491–6533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

