Coronary Thrombosis without Dissection following Blunt Trauma
- PMID: 27006836
- PMCID: PMC4781932
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/8671015
Coronary Thrombosis without Dissection following Blunt Trauma
Abstract
Blunt trauma to the chest resulting in coronary thrombosis and ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is a rare but well-described occurrence in adults. Angiography in such cases has generally disclosed complete epicardial coronary occlusion with thrombus, indistinguishable from the findings commonly found in spontaneous plaque rupture due to atherosclerotic disease. In all previously reported cases in which coronary interrogation with intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) was performed in association with acute revascularization, coronary artery dissection was implicated as the etiology of coronary thrombosis. We present the first case report of blunt trauma-associated coronary thrombosis without underlying atherosclerosis or coronary dissection, as documented by IVUS imaging.
Figures
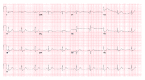

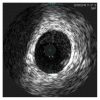
References
-
- Moore J. E. Acute apical myocardial infarction after blunt chest trauma incurred during a basketball game. Journal of the American Board of Family Practice. 2001;14(3):219–222. - PubMed
-
- Adler J. D., Scalea T. M. Right coronary artery dissection after blunt chest trauma. Injury Extra. 2010;41(8):77–79. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2010.04.022. - DOI
-
- Moreno R., Pérez del Todo J., Nieto M., et al. Primary stenting in acute myocardial infarction secondary to right coronary artery dissection following blunt chest trauma. Usefulness of intracoronary ultrasound. International Journal of Cardiology. 2005;103(2):209–211. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2004.06.021. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

