Effects of Plectin Depletion on Keratin Network Dynamics and Organization
- PMID: 27007410
- PMCID: PMC4805305
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149106
Effects of Plectin Depletion on Keratin Network Dynamics and Organization
Abstract
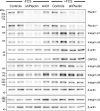
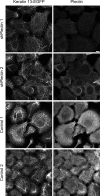
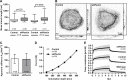
The keratin intermediate filament cytoskeleton protects epithelial cells against various types of stress and is involved in fundamental cellular processes such as signaling, differentiation and organelle trafficking. These functions rely on the cell type-specific arrangement and plasticity of the keratin system. It has been suggested that these properties are regulated by a complex cycle of assembly and disassembly. The exact mechanisms responsible for the underlying molecular processes, however, have not been clarified. Accumulating evidence implicates the cytolinker plectin in various aspects of the keratin cycle, i.e., by acting as a stabilizing anchor at hemidesmosomal adhesion sites and the nucleus, by affecting keratin bundling and branching and by linkage of keratins to actin filament and microtubule dynamics. In the present study we tested these hypotheses. To this end, plectin was downregulated by shRNA in vulvar carcinoma-derived A431 cells. As expected, integrin β4- and BPAG-1-positive hemidesmosomal structures were strongly reduced and cytosolic actin stress fibers were increased. In addition, integrins α3 and β1 were reduced. The experiments furthermore showed that loss of plectin led to a reduction in keratin filament branch length but did not alter overall mechanical properties as assessed by indentation analyses using atomic force microscopy and by displacement analyses of cytoplasmic superparamagnetic beads using magnetic tweezers. An increase in keratin movement was observed in plectin-depleted cells as was the case in control cells lacking hemidesmosome-like structures. Yet, keratin turnover was not significantly affected. We conclude that plectin alone is not needed for keratin assembly and disassembly and that other mechanisms exist to guarantee proper keratin cycling under steady state conditions in cultured single cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

