Using mitochondrial sirtuins as drug targets: disease implications and available compounds
- PMID: 27007507
- PMCID: PMC11108305
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-016-2180-7
Using mitochondrial sirtuins as drug targets: disease implications and available compounds
Abstract
Sirtuins are an evolutionary conserved family of NAD(+)-dependent protein lysine deacylases. Mammals have seven Sirtuin isoforms, Sirt1-7. They contribute to regulation of metabolism, stress responses, and aging processes, and are considered therapeutic targets for metabolic and aging-related diseases. While initial studies were focused on Sirt1 and 2, recent progress on the mitochondrial Sirtuins Sirt3, 4, and 5 has stimulated research and drug development for these isoforms. Here we review the roles of Sirtuins in regulating mitochondrial functions, with a focus on the mitochondrially located isoforms, and on their contributions to disease pathologies. We further summarize the compounds available for modulating the activity of these Sirtuins, again with a focus on mitochondrial isoforms, and we describe recent results important for the further improvement of compounds. This overview illustrates the potential of mitochondrial Sirtuins as drug targets and summarizes the status, progress, and challenges in developing small molecule compounds modulating their activity.
Keywords: Activator; Deacylase; Drug development; Inhibitor; Metabolic regulation; Sirt3; Sirt4; Sirt5.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

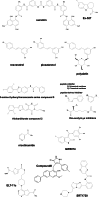

References
-
- Rauh D, Fischer F, Gertz M, Lakshminarasimhan M, Bergbrede T, Aladini F, Kambach C, Becker CFW, Zerweck J, Schutkowski M, Steegborn C. An acetylome peptide microarray reveals specificities and deacetylation substrates for all human sirtuin isoforms. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2327. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3327. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rardin MJ, Newman JC, Held JM, Cusack MP, Sorensen DJ, Li B, Schilling B, Mooney SD, Kahn CR, Verdin E, Gibson BW. Label-free quantitative proteomics of the lysine acetylome in mitochondria identifies substrates of SIRT3 in metabolic pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:6601–6606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1302961110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Still AJ, Floyd BJ, Hebert AS, Bingman CA, Carson JJ, Gunderson DR, Dolan BK, Grimsrud PA, Dittenhafer-Reed KE, Stapleton DS, Keller MP, Westphall MS, Denu JM, Attie AD, Coon JJ, Pagliarini DJ. Quantification of mitochondrial acetylation dynamics highlights prominent sites of metabolic regulation. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:26209–26219. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.483396. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

