Characterization of a Polyethylene Glycol-Amphotericin B Conjugate Loaded with Free AMB for Improved Antifungal Efficacy
- PMID: 27008086
- PMCID: PMC4805162
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152112
Characterization of a Polyethylene Glycol-Amphotericin B Conjugate Loaded with Free AMB for Improved Antifungal Efficacy
Erratum in
-
Correction: Characterization of a Polyethylene Glycol-Amphotericin B Conjugate Loaded with Free AMB for Improved Antifungal Efficacy.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 23;19(7):e0307862. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307862. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39042654 Free PMC article.
Abstract
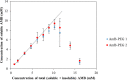
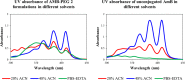
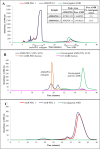
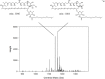
Amphotericin B (AMB) is a highly hydrophobic antifungal, whose use is limited by its toxicity and poor solubility. To improve its solubility, AMB was reacted with a functionalized polyethylene glycol (PEG), yielding soluble complex AmB-PEG formulations that theoretically comprise of chemically conjugated AMB-PEG and free AMB that is physically associated with the conjugate. Reverse-phase chromatography and size exclusion chromatography methods using HPLC were developed to separate conjugated AMB-PEG and free AmB, enabling the further characterization of these formulations. Using HPLC and dynamic light scattering analyses, it was observed that the AMB-PEG 2 formulation, having a higher molar ratio of 2 AMB: 1 PEG, possesses more free AMB and has relatively larger particle diameters compared to the AMB-PEG 1 formulation, that consists of 1 AMB: 1 PEG. The identity of the conjugate was also verified using mass spectrometry. AMB-PEG 2 demonstrates improved antifungal efficacy relative to AMB-PEG 1, without a concurrent increase in in vitro toxicity to mammalian cells, implying that the additional loading of free AMB in the AMB-PEG formulation can potentially increase its therapeutic index. Compared to unconjugated AMB, AMB-PEG formulations are less toxic to mammalian cells in vitro, even though their MIC50 values are comparatively higher in a variety of fungal strains tested. Our in vitro results suggest that AMB-PEG 2 formulations are two times less toxic than unconjugated AMB with antifungal efficacy on Candida albicans and Cryptococcus neoformans.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Assessment of in vitro antifungal efficacy and in vivo toxicity of Amphotericin B-loaded PLGA and PLGA-PEG blend nanoparticles.J Mycol Med. 2017 Dec;27(4):519-529. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2017.07.004. Epub 2017 Aug 8. J Mycol Med. 2017. PMID: 28797532
-
Reformulation of Fungizone by PEG-DSPE Micelles: Deaggregation and Detoxification of Amphotericin B.Pharm Res. 2016 Sep;33(9):2098-106. doi: 10.1007/s11095-016-1948-7. Epub 2016 May 19. Pharm Res. 2016. PMID: 27198671 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization, stabilization, and characterization of amphotericin B loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for ocular drug delivery.Int J Pharm. 2019 Dec 15;572:118771. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118771. Epub 2019 Oct 26. Int J Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31669555 Free PMC article.
-
Oral administration of amphotericin B nanoparticles: antifungal activity, bioavailability and toxicity in rats.Drug Deliv. 2017 Nov;24(1):40-50. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2016.1228715. Drug Deliv. 2017. PMID: 28155565 Free PMC article.
-
Amphotericin B formulations: a comparative review of efficacy and toxicity.Drugs. 2013 Jun;73(9):919-34. doi: 10.1007/s40265-013-0069-4. Drugs. 2013. PMID: 23729001 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Novel Amphotericin B-Immobilized Nitric Oxide-Releasing Platform for the Prevention of Broad-Spectrum Infections and Thrombosis.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021 May 5;13(17):19613-19624. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c01330. Epub 2021 Apr 27. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021. PMID: 33904311 Free PMC article.
-
"Click" amphotericin B in prodrug nanoformulations for enhanced systemic fungemia treatment.J Control Release. 2024 Jun;370:626-642. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.05.003. Epub 2024 May 15. J Control Release. 2024. PMID: 38734314 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, characterization, and mechanistic studies of a gold nanoparticle-amphotericin B covalent conjugate with enhanced antileishmanial efficacy and reduced cytotoxicity.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Aug 20;14:6073-6101. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S196421. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31686803 Free PMC article.
-
Design of an Antifungal Surface Embedding Liposomal Amphotericin B Through a Mussel Adhesive-Inspired Coating Strategy.Front Chem. 2019 Jun 18;7:431. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00431. eCollection 2019. Front Chem. 2019. PMID: 31275922 Free PMC article.
-
Oral delivery of brain-targeted miltefosine-loaded alginate nanoparticles functionalized with polysorbate 80 for the treatment of cryptococcal meningitis.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2023 Apr 3;78(4):1092-1101. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkad053. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2023. PMID: 36881722 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ellis D. Amphotericin B: spectrum and resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2002;49 Suppl 1: 7–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

