Kidneys: key modulators of high-density lipoprotein levels and function
- PMID: 27008596
- PMCID: PMC4899840
- DOI: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000217
Kidneys: key modulators of high-density lipoprotein levels and function
Abstract
Purpose of review: The review will examine advances in our understanding of the role kidneys play in high-density lipoprotein (HDL) metabolism and the effect on levels, composition, and function of HDL particles.
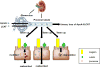
Recent findings: Components of the HDL particles can cross the glomerular filtration barrier. Some of these components, including apolipoproteins and enzymes involved in lipid metabolism, are taken up by the proximal tubule and degraded, modified, salvaged/returned to the circulation, or lost in the urine. Injury of the glomerular capillaries or tubules can affect these intrarenal processes and modify HDL. Changes in the plasma and urine levels of HDL may be novel markers of kidney damage or mechanism(s) of kidney disease.
Summary: The kidneys have a significant role in the metabolism of individual HDL components, which in turn modulate HDL levels, composition, and functionality of HDL particles. These intrarenal effects may be useful markers of kidney damage and have consequences on kidney-related perturbations in HDL.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: There are no conflicts.
Figures
References
-
- Zhong J, Yang H, Tsuchida Y, et al. Podocyte and tubule injury have different effects on renal handling of apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I) and its receptors. ASN Kidney Week 2015; San Diego, CA, USA. 2015.
-
- Hammad SM, Barth JL, Knaak C, et al. Megalin acts in concert with cubilin to mediate endocytosis of high density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:12003–12008. - PubMed
-
- Graversen JH, Castro G, Kandoussi A, et al. A pivotal role of the human kidney in catabolism of HDL protein components apolipoprotein A-I and A-IV but not of A-II. Lipids. 2008;43:467–470. - PubMed
-
- Aseem O, Smith BT, Cooley MA, et al. Cubilin maintains blood levels of HDL and albumin. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;25:1028–1036. *The study shows that cubilin deficiency in the proximal tubule reduces uptake of ApoA-I and albumin which is tied to decreased levels of plasma albumin, ApoA-I, and HDL. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

