Emodin Bidirectionally Modulates Macrophage Polarization and Epigenetically Regulates Macrophage Memory
- PMID: 27008857
- PMCID: PMC4882421
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.702092
Emodin Bidirectionally Modulates Macrophage Polarization and Epigenetically Regulates Macrophage Memory
Abstract
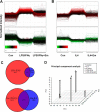
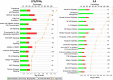
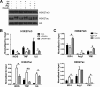
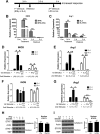
Macrophages are pleiotropic cells capable of performing a broad spectrum of functions. Macrophage phenotypes are classified along a continuum between the extremes of proinflammatory M1 macrophages and anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages. The seemingly opposing functions of M1 and M2 macrophages must be tightly regulated for an effective and proper response to foreign molecules or damaged tissue. Excessive activation of either M1 or M2 macrophages contributes to the pathology of many diseases. Emodin is a Chinese herb-derived compound and has shown potential to inhibit inflammation in various settings. In this study, we tested the ability of emodin to modulate the macrophage response to both M1 and M2 stimuli. Primary mouse macrophages were stimulated with LPS/IFNγ or IL4 with or without emodin, and the effects of emodin on gene transcription, cell signaling pathways, and histone modifications were examined by a variety of approaches, including microarray, quantitative real-time PCR, Western blotting, chromatin immunoprecipitation, and functional assays. We found that emodin bidirectionally tunes the induction of LPS/IFNγ- and IL4-responsive genes through inhibiting NFκB/IRF5/STAT1 signaling and IRF4/STAT6 signaling, respectively. Thereby, emodin modulates macrophage phagocytosis, migration, and NO production. Furthermore, emodin inhibited the removal of H3K27 trimethylation (H3K27m3) marks and the addition of H3K27 acetylation (H3K27ac) marks on genes required for M1 or M2 polarization of macrophages. In conclusion, our data suggest that emodin is uniquely able to suppress the excessive response of macrophages to both M1 and M2 stimuli and therefore has the potential to restore macrophage homeostasis in various pathologies.
Keywords: cell signaling; emodin; histone modification; inflammation; innate immunity; macrophage; macrophage memory; polarization.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Tribbles homolog 1 deficiency modulates function and polarization of murine bone marrow-derived macrophages.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jul 20;293(29):11527-11536. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000703. Epub 2018 Jun 13. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29899113 Free PMC article.
-
Emodin Inhibits Breast Cancer Growth by Blocking the Tumor-Promoting Feedforward Loop between Cancer Cells and Macrophages.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Aug;15(8):1931-42. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0987. Epub 2016 May 18. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 27196773 Free PMC article.
-
Pinosylvin Shifts Macrophage Polarization to Support Resolution of Inflammation.Molecules. 2021 May 8;26(9):2772. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092772. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34066748 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA-Mediated Macrophage Polarization and its Potential Role in the Regulation of Inflammatory Response.Shock. 2016 Aug;46(2):122-31. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000604. Shock. 2016. PMID: 26954942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of M1 and M2 macrophage polarization by metformin: Implications for inflammatory diseases and malignant tumors.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Apr 4;151:114345. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114345. Epub 2025 Mar 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40024215 Review.
Cited by
-
The Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Phytochemicals and Their Effects on Epigenetic Mechanisms Involved in TLR4/NF-κB-Mediated Inflammation.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 26;12:606069. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.606069. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33868227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of histone acetylation in a murine model of allergic asthma by proteomic analysis.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Apr;246(8):929-939. doi: 10.1177/1535370220980345. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 33327783 Free PMC article.
-
Trained immunity in monocyte/macrophage: Novel mechanism of phytochemicals in the treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 21;14:1109576. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1109576. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36895942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emodin alleviates hypertrophic scar formation by suppressing macrophage polarization and inhibiting the Notch and TGF-β pathways in macrophages.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021 Jul 23;54(8):e11184. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2021e11184. eCollection 2021. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021. PMID: 34320121 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of Plant-Derived Compounds in Preventing and Reversing Organ Fibrosis and the Underlying Mechanisms.Cells. 2024 Feb 28;13(5):421. doi: 10.3390/cells13050421. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38474385 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhou D., Huang C., Lin Z., Zhan S., Kong L., Fang C., and Li J. (2014) Macrophage polarization and function with emphasis on the evolving roles of coordinated regulation of cellular signaling pathways. Cell Signal. 26, 192–197 - PubMed
-
- Lawrence T., and Natoli G. (2011) Transcriptional regulation of macrophage polarization: enabling diversity with identity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 11, 750–761 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

