Low dose of lenalidmide and PI3K/mTOR inhibitor trigger synergistic cytoxicity in activated B cell-like subtype of diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- PMID: 27009084
- PMCID: PMC4806505
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-016-0327-x
Low dose of lenalidmide and PI3K/mTOR inhibitor trigger synergistic cytoxicity in activated B cell-like subtype of diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Abstract
Background: Activated B cell-like subtype of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (ABC-DLBCL) presents aggressive clinical courses and poor prognosis. Targeting key pathways may raise the possibility of improving clinical outcomes.
Methods: The synergetic effects were assessed by CCK-8 assay and measured by isobologram analysis. The NVP-Bez235 and lenalidomide cytotoxicity were measured by flow cytometry, Western Blot and si-RNA transfection. The combined treatment inducing tumor regression in vivo was performed in nude mice of OCI-Ly10 xenograft mouse model.
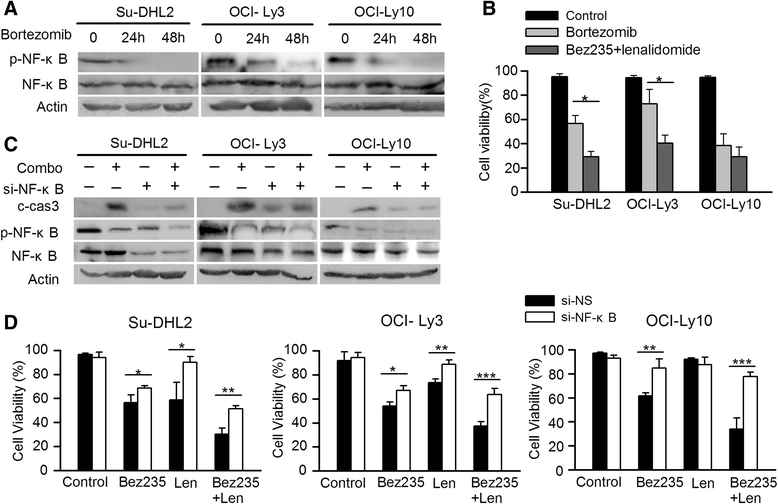
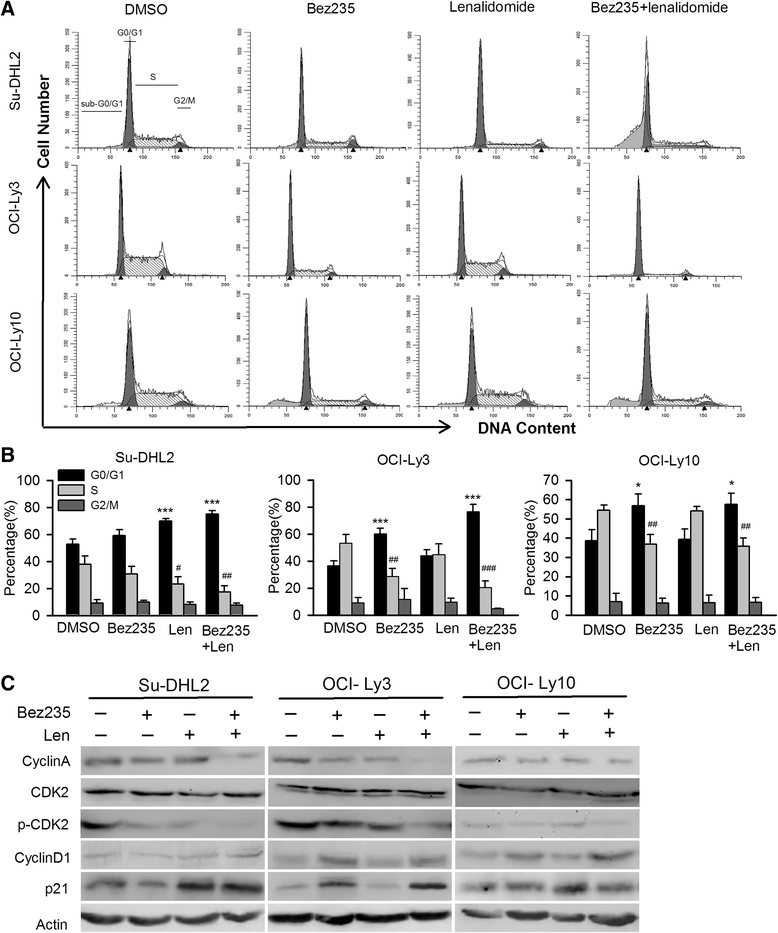
Results: Low dose of two agents represented significant inhibition of proliferation with CI value < 1. NVP-Bez235 combined with lenalidomide remarkably increased apoptosis through intrinsic pathway by upregulating Bim, Bax and downregulating Bcl-xL. Akt, especially NF-κB, played an important role in the synergetic effects. Cotreatment also induced the cell cycle to be arrested in G0/G1 phase, and decreased S phase by increasing p21 expression, downregulating cyclinA and diminishing CDK2 phosphorylation in Su-DHL2 and OCI-Ly3 but not in OCI-Ly10. Mice treated with NVP-Bez235/lenalidomide represented obvious tumor growth regression and prolonged overall survival.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrated the synergistic effect of low dose of NVP-Bez235 and lenalidomide in ABC-DLBCL, the underlying mechanism may be multifunctional, involving apoptosis, Akt and NF-κB inactivation and cell cycle arrest. Cotreatment was also effective in vivo. These data pave the way for potential treatment of ABC-DLBCL with combination of NVP-Bez235 and lenalidomide.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cell cycle; Diffuse large B cell lymphoma; Lenalidomide; NF-κB; PI3K/mTOR inhibitor.
Figures





References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Feugier P, Van Hoof A, Sebban C, Solal-Celigny P, Bouabdallah R, Ferme C, et al. Long-term results of the R-CHOP study in the treatment of elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a study by the Groupe d’Etude des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2005;23:4117–26. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.09.131. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nowakowski GS, LaPlant B, Macon WR, Reeder CB, Foran JM, Nelson GD, et al. Lenalidomide combined with R-CHOP overcomes negative prognostic impact of non-germinal center B-cell phenotype in newly diagnosed diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma: a phase II study. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2015;33:251–7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.55.5714. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

