Hypertension: the missing WNKs
- PMID: 27009339
- PMCID: PMC4967160
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00358.2015
Hypertension: the missing WNKs
Abstract
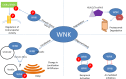
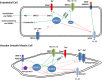
The With no Lysine [K] (WNK) family of enzymes are central in the regulation of blood pressure. WNKs have been implicated in hereditary hypertension disorders, mainly through control of the activity and levels of ion cotransporters and channels. Actions of WNKs in the kidney have been heavily investigated, and recent studies have provided insight into not only the regulation of these enzymes but also how mutations in WNKs and their interacting partners contribute to hypertensive disorders. Defining the roles of WNKs in the cardiovascular system will provide clues about additional mechanisms by which WNKs can regulate blood pressure. This review summarizes recent developments in the regulation of the WNK signaling cascade and its role in regulation of blood pressure.
Keywords: WNK; cardiovascular; hypertension.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
The evolving field of salt transport regulation in the Steve Hebert Lecture.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Jul 1;311(1):F68-70. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00229.2016. Epub 2016 May 4. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27147671 No abstract available.
References
-
- Adragna NC, White RE, Orlov SN, Lauf PK. K-Cl cotransport in vascular smooth muscle and erythrocytes: possible implication in vasodilation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 278: C381–C390, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Akar F, Jiang G, Paul RJ, O'Neill WC. Contractile regulation of the Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransporter in vascular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281: C579–C584, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Akar F, Skinner E, Klein JD, Jena M, Paul RJ, O'Neill WC. Vasoconstrictors and nitrovasodilators reciprocally regulate the Na+-K+-2Cl− cotransporter in rat aorta. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 276: C1383–C1390, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Anderica-Romero AC, Escobar L, Padilla-Flores T, Pedraza-Chaverri J. Insights in cullin 3/WNK4 and its relationship to blood pressure regulation and electrolyte homeostasis. Cell Signal 26: 1166–1172, 2014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

