Proximal tubule-specific glutamine synthetase deletion alters basal and acidosis-stimulated ammonia metabolism
- PMID: 27009341
- PMCID: PMC4935770
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00547.2015
Proximal tubule-specific glutamine synthetase deletion alters basal and acidosis-stimulated ammonia metabolism
Abstract
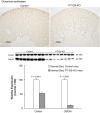
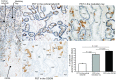
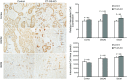
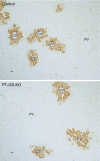
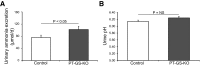
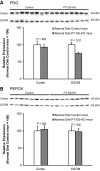
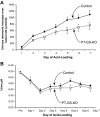
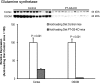
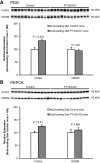
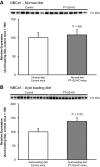
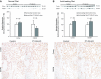
Glutamine synthetase (GS) catalyzes the recycling of NH4 (+) with glutamate to form glutamine. GS is highly expressed in the renal proximal tubule (PT), suggesting ammonia recycling via GS could decrease net ammoniagenesis and thereby limit ammonia available for net acid excretion. The purpose of the present study was to determine the role of PT GS in ammonia metabolism under basal conditions and during metabolic acidosis. We generated mice with PT-specific GS deletion (PT-GS-KO) using Cre-loxP techniques. Under basal conditions, PT-GS-KO increased urinary ammonia excretion significantly. Increased ammonia excretion occurred despite decreased expression of key proteins involved in renal ammonia generation. After the induction of metabolic acidosis, the ability to increase ammonia excretion was impaired significantly by PT-GS-KO. The blunted increase in ammonia excretion occurred despite greater expression of multiple components of ammonia generation, including SN1 (Slc38a3), phosphate-dependent glutaminase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, and Na(+)-coupled electrogenic bicarbonate cotransporter. We conclude that 1) GS-mediated ammonia recycling in the PT contributes to both basal and acidosis-stimulated ammonia metabolism and 2) adaptive changes in other proteins involved in ammonia metabolism occur in response to PT-GS-KO and cause an underestimation of the role of PT GS expression.
Keywords: acid-base; ammonia; glutamine synthetase; proximal tubule.
Figures


References
-
- Biver S, Belge H, Bourgeois S, Van Vooren P, Nowik M, Scohy S, Houillier P, Szpirer J, Szpirer C, Wagner CA, Devuyst O, Marini AM. A role for Rhesus factor Rhcg in renal ammonium excretion and male fertility. Nature 456: 339–343, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Boulland JL, Osen KK, Levy LM, Danbolt NC, Edwards RH, Storm-Mathisen J, Chaudhry FA. Cell-specific expression of the glutamine transporter SN1 suggests differences in dependence on the glutamine cycle. Eur J Neurosci 15: 1615–1631, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Busque SM, Wagner CA. Potassium restriction, high protein intake, and metabolic acidosis increase expression of the glutamine transporter SNAT3 (Slc38a3) in mouse kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297: F440–F450, 2009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

