Spin-Current and Spin-Splitting in Helicoidal Molecules Due to Spin-Orbit Coupling
- PMID: 27009836
- PMCID: PMC4806306
- DOI: 10.1038/srep23452
Spin-Current and Spin-Splitting in Helicoidal Molecules Due to Spin-Orbit Coupling
Abstract
The use of organic materials in spintronic devices has been seriously considered after recent experimental works have shown unexpected spin-dependent electrical properties. The basis for the confection of any spintronic device is ability of selecting the appropriated spin polarization. In this direction, DNA has been pointed out as a potential candidate for spin selection due to the spin-orbit coupling originating from the electric field generated by accumulated electrical charges along the helix. Here, we demonstrate that spin-orbit coupling is the minimum ingredient necessary to promote a spatial spin separation and the generation of spin-current. We show that the up and down spin components have different velocities that give rise to a spin-current. By using a simple situation where spin-orbit coupling is present, we provide qualitative justifications to our results that clearly point to helicoidal molecules as serious candidates to integrate spintronic devices.
Figures
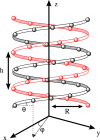

 ,
,  ,
,  , η = 0.3 eV, θ = 0.66 and
, η = 0.3 eV, θ = 0.66 and  and tSO = 0.03 eV. The up and down spinor components are represented by red and blue, respectively.
and tSO = 0.03 eV. The up and down spinor components are represented by red and blue, respectively.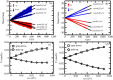
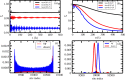
 and
and  , of an initially gaussian wave packet, in a double strand molecule, with width (a) l = 1 and (b) l = 30 for three spin-orbit coupling constant: tso = 0.01, tso = 0.02 and tso = 0.03 eV. (c,d) are, respectively, the mean velocity of the wave packet components for the cases studied in (a,b).
, of an initially gaussian wave packet, in a double strand molecule, with width (a) l = 1 and (b) l = 30 for three spin-orbit coupling constant: tso = 0.01, tso = 0.02 and tso = 0.03 eV. (c,d) are, respectively, the mean velocity of the wave packet components for the cases studied in (a,b).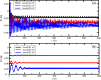
References
-
- Wolf S. A., Awshalom D. D., Buhrman R. A., Daughton J. M., von Molnár S., Roukes M. L., Chtchelkanova A. Y. & Treger D. M. Spintronics: A Spin-Based Electronics Vision for the Future, Science 294, 1488–1495 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Datta S. & Das B. Electronic analog of electro-optic modulator, Appl. Phys. Lett. 56, 665–667 (1990).
-
- Lu J. P., Yau J. B., Shukla S. P., Shayegan M., Wissinger L., Rössler & Winkler R. Tunable Spin-Splitting and Spin-Resolved Ballistic Transport in GaAs/AlGaAs Two-Dimensional Holes, Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 1282–1285 (1998).
-
- Jungwirth T., Wunderlich J. & Olejník K. Spin Hall effect devices, Nature Materials 11, 382–390 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Sanvito S. Molecular spintronics, Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 3336–3355 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

