LIG4 mediates Wnt signalling-induced radioresistance
- PMID: 27009971
- PMCID: PMC4820809
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10994
LIG4 mediates Wnt signalling-induced radioresistance
Abstract
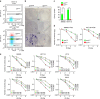
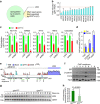
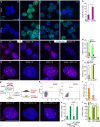
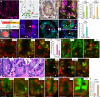
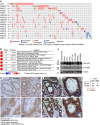
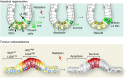
Despite the implication of Wnt signalling in radioresistance, the underlying mechanisms are unknown. Here we find that high Wnt signalling is associated with radioresistance in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells and intestinal stem cells (ISCs). We find that LIG4, a DNA ligase in DNA double-strand break repair, is a direct target of β-catenin. Wnt signalling enhances non-homologous end-joining repair in CRC, which is mediated by LIG4 transactivated by β-catenin. During radiation-induced intestinal regeneration, LIG4 mainly expressed in the crypts is conditionally upregulated in ISCs, accompanied by Wnt/β-catenin signalling activation. Importantly, among the DNA repair genes, LIG4 is highly upregulated in human CRC cells, in correlation with β-catenin hyperactivation. Furthermore, blocking LIG4 sensitizes CRC cells to radiation. Our results reveal the molecular mechanism of Wnt signalling-induced radioresistance in CRC and ISCs, and further unveils the unexpected convergence between Wnt signalling and DNA repair pathways in tumorigenesis and tissue regeneration.
Figures

References
-
- Clevers H., Loh K. M. & Nusse R. Stem cell signaling. An integral program for tissue renewal and regeneration: Wnt signaling and stem cell control. Science 346, 1248012 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Clevers H. & Nusse R. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 149, 1192–1205 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Clements W. M., Lowy A. M. & Groden J. Adenomatous polyposis coli/beta-catenin interaction and downstream targets: altered gene expression in gastrointestinal tumors. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 3, 113–120 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Su L. K. et al. Multiple intestinal neoplasia caused by a mutation in the murine homolog of the APC gene. Science 256, 668–670 (1992). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

