2,5-hexanedione induced apoptosis of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by reactive oxygen species
- PMID: 27010086
- PMCID: PMC5356963
- DOI: 10.1539/joh.15-0143-OA
2,5-hexanedione induced apoptosis of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by reactive oxygen species
Abstract
Objectives: n-Hexane, a common industrial organic solvent, causes multiple organ damage, especially neurotoxicity, which is proved to be caused by its metabolite 2,5-hexanedione (2,5-HD). We previously showed that 2,5-HD induced apoptosis of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs). In the current study, we explored the mechanism of 2,5-HD-induced apoptosis, especially the role played by reactive oxygen species (ROS).
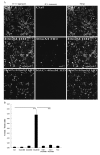
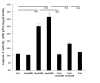
Methods: Intracellular ROS levels after 2,5-HD treatment were measured by the dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) method, and the antioxidant N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) was used to scavenge ROS. Apoptosis, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), and caspase-3 activity were measured after 2,5-HD exposure with or without NAC pretreatment.
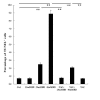
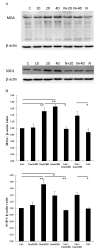
Results: In rat BMSCs, 20 mM 2,5-HD significantly increased ROS levels and apoptosis. In addition, MMP activity was decreased and caspase-3 activity was increased. With NAC pretreatment, ROS increases were prevented, cells were rescued from apoptosis, and both MMP and caspase-3 activity returned to normal levels. Western blotting analysis of malondialdehyde-modified proteins and superoxide dismutase (SOD) 1 showed that after 2,5-HD exposure, BMSCs had oxidative damage and abnormal SOD1 expression. These returned to normal when cells were pretreated with NAC in addition to 20 mM 2,5-HD. Furthermore, the expressions of NF-κB p65/RelA and phospho-NF-κB p65/RelA (Ser536) were suppressed after 2,5-HD exposure and restored by NAC pretreatment.
Conclusions: 2,5-HD-induced apoptosis in rat BMSCs is potentially mediated by excessive ROS production.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Huang CC. Polyneuropathy induced by n-hexane intoxication in Taiwan. Acta Neurol Taiwan 2008; 17: 3-10. - PubMed
-
- Neghab M, Soleimani E, Khamoushian K. Electrophysiological studies of shoemakers exposed to sub-TLV levels of n-hexane. J Occup Health 2012; 54: 376-382. - PubMed
-
- Kim MS, Park HR, Park M, et al. Neurotoxic effect of 2,5-hexanedione on neural progenitor cells and hippocampal neurogenesis. Toxicology 2009; 260: 97-103. - PubMed
-
- LoPachin RM, DeCaprio AP. gamma-Diketone neuropathy: axon atrophy and the role of cytoskeletal protein adduction. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2004; 199: 20-34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

