Survival of encapsulated islets: More than a membrane story
- PMID: 27011906
- PMCID: PMC4801806
- DOI: 10.5500/wjt.v6.i1.69
Survival of encapsulated islets: More than a membrane story
Abstract
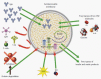
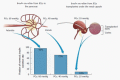
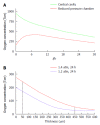
At present, proven clinical treatments but no cures are available for diabetes, a global epidemic with a huge economic burden. Transplantation of islets of Langerhans by their infusion into vascularized organs is an experimental clinical protocol, the first approach to attain cure. However, it is associated with lifelong use of immunosuppressants. To overcome the need for immunosuppression, islets are encapsulated and separated from the host immune system by a permselective membrane. The lead material for this application is alginate which was tested in many animal models and a few clinical trials. This review discusses all aspects related to the function of transplanted encapsulated islets such as the basic requirements from a permselective membrane (e.g., allowable hydrodynamic radii, implications of the thickness of the membrane and relative electrical charge). Another aspect involves adequate oxygen supply, which is essential for survival/performance of transplanted islets, especially when using large retrievable macro-capsules implanted in poorly oxygenated sites like the subcutis. Notably, islets can survive under low oxygen tension and are physiologically active at > 40 Torr. Surprisingly, when densely crowded, islets are fully functional under hyperoxic pressure of up to 500 Torr (> 300% of atmospheric oxygen tension). The review also addresses an additional category of requirements for optimal performance of transplanted islets, named auxiliary technologies. These include control of inflammation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and the intra-capsular environment. The review highlights that curing diabetes with a functional bio-artificial pancreas requires optimizing all of these aspects, and that significant advances have already been made in many of them.
Keywords: Bio-artificial pancreas; Diabetes; Encapsulation; Islets of Langerhans; Oxygen supply; Permselective membrane; Transplantation.
Figures




References
-
- Dall TM, Yang W, Halder P, Pang B, Massoudi M, Wintfeld N, Semilla AP, Franz J, Hogan PF. The economic burden of elevated blood glucose levels in 2012: diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes, gestational diabetes mellitus, and prediabetes. Diabetes Care. 2014;37:3172–3179. - PubMed
-
- Ehehalt S, Dietz K, Willasch AM, Neu A; DIARY-Group Baden-Wuerttemberg. Prediction model for the incidence and prevalence of type 1 diabetes in childhood and adolescence: evidence for a cohort-dependent increase within the next two decades in Germany. Pediatr Diabetes. 2012;13:15–20. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Ryan EA, Korbutt GS, Toth E, Warnock GL, Kneteman NM, Rajotte RV. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:230–238. - PubMed
-
- Collaborative Island Transplant Registry (CITR) eighth annual report 2013. [Accessed 2015 Aug 1] Available from: http://www.citregistry.org.
-
- Matsumoto S, Tan P, Baker J, Durbin K, Tomiya M, Azuma K, Doi M, Elliott RB. Clinical porcine islet xenotransplantation under comprehensive regulation. Transplant Proc. 2014;46:1992–1995. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

