Interaction between castanospermine an immunosuppressant and cyclosporin A in rat cardiac transplantation
- PMID: 27011919
- PMCID: PMC4801797
- DOI: 10.5500/wjt.v6.i1.206
Interaction between castanospermine an immunosuppressant and cyclosporin A in rat cardiac transplantation
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the interaction between castanospermine and cyclosporin A (CsA) and to provide an explanation for it.
Methods: The alkaloid castanospermine was prepared from the seeds of Castanospermum austral consistently achieving purity. Rat heterotopic cardiac transplantation and mixed lymphocyte reactivity were done using genetically inbred strains of PVG (donor) and DA (recipient). For the mixed lymphocyte reaction stimulator cells were irradiated with 3000 rads using a linear accelerator. Cyclosporin A was administered by gavage and venous blood collected 2 h later (C2). The blood levels of CsA (Neoral) were measured by immunoassay which consisted of a homogeneous enzyme assay (EMIT) on Cobas Mira. Statistical analyses of interactions were done by an accelerated failure time model with Weibull distribution for allograft survival and logistic regression for the mixed lymphocyte reactivity.
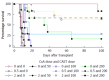
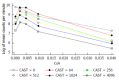
Results: Castanospermine prolonged transplant survival times as a function of dose even at relatively low doses. Cyclosporin A also prolonged transplant survival times as a function of dose particularly at doses above 2 mg/kg. There were synergistic interactions between castanospermine and CsA in the prolongation of cardiac allograft survival for dose ranges of CsA by castanospermine of (0 to 2) mg/kg by (0 to 200) mg/kg (HR = 0.986; 95%CI: 0.981-0.992; P < 0.001) and (0 to 3) mg/kg by (0 to 100) mg/kg (HR = 0.986; 95%CI: 0.981-0.992; P < 0.001) respectively. The addition of castanospermine did not significantly increase the levels of cyclosporin A on day 3 or day 6 for all doses of CsA. On the contrary, cessation of castanospermine in the presence of CsA at 2 mg/kg significantly increased the CsA level (P = 0.002). Castanospermine inhibited mixed lymphocyte reactivity in a dose dependent manner but without synergistic interaction.
Conclusion: There is synergistic interaction between castanospermine and CsA in rat cardiac transplantation. Neither the mixed lymphocyte reaction nor the metabolism of CsA provides an explanation.
Keywords: Cardiac transplantation; Castanospermine; Cyclosporin A; Mixed lymphocyte reaction; Positive interaction.
Figures

References
-
- Vajdic CM, McDonald SP, McCredie MR, van Leeuwen MT, Stewart JH, Law M, Chapman JR, Webster AC, Kaldor JM, Grulich AE. Cancer incidence before and after kidney transplantation. JAMA. 2006;296:2823–2831. - PubMed
-
- Mueller NJ. New immunosuppressive strategies and the risk of infection. Transpl Infect Dis. 2008;10:379–384. - PubMed
-
- Flechner SM, Kobashigawa J, Klintmalm G. Calcineurin inhibitor-sparing regimens in solid organ transplantation: focus on improving renal function and nephrotoxicity. Clin Transplant. 2008;22:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Bodziak KA, Hricik DE. New-onset diabetes mellitus after solid organ transplantation. Transpl Int. 2009;22:519–530. - PubMed
-
- Elbein AD. Glycosidase inhibitors: inhibitors of N-linked oligosaccharide processing. FASEB J. 1991;5:3055–3063. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

