Epidemiology, Genetic Recombination, and Pathogenesis of Coronaviruses
- PMID: 27012512
- PMCID: PMC7125511
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tim.2016.03.003
Epidemiology, Genetic Recombination, and Pathogenesis of Coronaviruses
Abstract
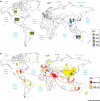
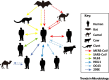
Human coronaviruses (HCoVs) were first described in the 1960s for patients with the common cold. Since then, more HCoVs have been discovered, including those that cause severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), two pathogens that, upon infection, can cause fatal respiratory disease in humans. It was recently discovered that dromedary camels in Saudi Arabia harbor three different HCoV species, including a dominant MERS HCoV lineage that was responsible for the outbreaks in the Middle East and South Korea during 2015. In this review we aim to compare and contrast the different HCoVs with regard to epidemiology and pathogenesis, in addition to the virus evolution and recombination events which have, on occasion, resulted in outbreaks amongst humans.
Keywords: MERS; SARS; coronavirus; evolution; pathogenesis; recombination.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Global interim guidance on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) during pregnancy and puerperium from FIGO and allied partners: Information for healthcare professionals.Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2020 Jun;149(3):273-286. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.13156. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2020. PMID: 32248521 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigating the threat of emerging infectious diseases; a coevolutionary perspective.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):1288-1295. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1920741. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 33957064 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lai M. Coronaviridae. In: Knipe D.M., Howley P.M., editors. Fields Virology. 5th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 1305–1335.
-
- Durham P.J. Rotavirus and coronavirus associated diarrhoea in domestic animals. N. Zealand Vet. J. 1979;27:30–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

