ATRA transcriptionally induces nSMase2 through CBP/p300-mediated histone acetylation
- PMID: 27013100
- PMCID: PMC4847633
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M067447
ATRA transcriptionally induces nSMase2 through CBP/p300-mediated histone acetylation
Abstract
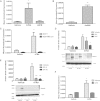
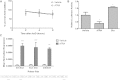
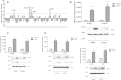
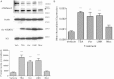
Neutral sphingomyelinase-2 (nSMase2) is a key ceramide-producing enzyme in cellular stress responses. While many posttranslational regulators of nSMase2 are known, emerging evidence suggests a more protracted regulation of nSMase2 at the transcriptional level. Previously, we reported that nSMase2 is induced by all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) in MCF7 cells and implicated nSMase2 in ATRA-induced growth arrest. Here, we further investigated how ATRA regulates nSMase2. We find that ATRA regulates nSMase2 transcriptionally through the retinoic acid receptor-α, but this is independent of previously identified transcriptional regulators of nSMase2 (Sp1, Sp3, Runx2) and is not through increased promoter activity. Epigenetically, the nSMase2 gene is not repressively methylated in MCF7 cells. However, inhibition of histone deacetylases (HDACs) with trichostatin A (TSA) induced nSMase2 comparably to ATRA; furthermore, combined ATRA and TSA treatment was not additive, suggesting ATRA regulates nSMase2 through direct modulation of histone acetylation. Confirming this, the histone acetyltransferases CREB-binding protein and p300 were required for ATRA induction of nSMase2. Finally, use of class-specific HDAC inhibitors suggested that HDAC4 and/or HDAC5 are negative regulators of nSMase2 expression. Collectively, these results identify a novel pathway of nSMase2 regulation and suggest that physiological or pharmacological modulation of histone acetylation can directly affect nSMase2 levels.
Keywords: all-trans retinoic acid; epigenetic; histone acetyltransferase; histone deacetylase; neutral sphingomyelinase-2; nuclear receptors; retinoids; signal transduction; sphingolipids; transcription.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Transcriptional regulation of neutral sphingomyelinase 2 in all-trans retinoic acid-treated human breast cancer cell line, MCF-7.J Biochem. 2012 Jun;151(6):599-610. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvs037. Epub 2012 Apr 11. J Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22496486
-
Retinoic acids and trichostatin A (TSA), a histone deacetylase inhibitor, induce human pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4) gene expression.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Mar-Apr;1759(3-4):141-51. doi: 10.1016/j.bbaexp.2006.04.005. Epub 2006 Apr 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16757381
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors modulate the transcriptional regulation of guanylyl cyclase/natriuretic peptide receptor-a gene: interactive roles of modified histones, histone acetyltransferase, p300, AND Sp1.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 7;289(10):6991-7002. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.511444. Epub 2014 Jan 22. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24451378 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of airway inflammation.Curr Opin Immunol. 2007 Dec;19(6):694-700. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2007.07.016. Epub 2007 Aug 27. Curr Opin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17720468 Review.
-
Modulation of gene expression dynamics by co-transcriptional histone methylations.Exp Mol Med. 2017 Apr 28;49(4):e326. doi: 10.1038/emm.2017.19. Exp Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28450734 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-1 as a Key Epigenetic Regulator in Early Differentiation of Cardiac Sinoatrial Region.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 15;25(12):6608. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126608. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928314 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingolipids and their metabolism in physiology and disease.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Mar;19(3):175-191. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.107. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29165427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics and Sphingolipid Metabolism in Health and Disease.Int J Biopharm Sci. 2018 Oct;1(2):105. doi: 10.31021/ijbs.20181105. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Int J Biopharm Sci. 2018. PMID: 30637412 Free PMC article.
-
Combinational therapy of all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and sphingomyelin induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in B16F10 melanoma cancer cells.Turk J Biol. 2024 Oct 14;48(6):401-413. doi: 10.55730/1300-0152.2715. eCollection 2024. Turk J Biol. 2024. PMID: 39758841 Free PMC article.
-
Insights Into the Function and Clinical Application of HDAC5 in Cancer Management.Front Oncol. 2021 Jun 10;11:661620. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.661620. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34178647 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hannun Y. A., and Obeid L. M.. 2008. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9: 139–150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

