Meiotic recombination and the crossover assurance checkpoint in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 27013114
- PMCID: PMC5082714
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.03.014
Meiotic recombination and the crossover assurance checkpoint in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
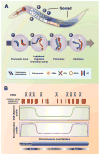
During meiotic prophase, chromosomes pair and synapse with their homologs and undergo programmed DNA double-strand break (DSB) formation to initiate meiotic recombination. These DSBs are processed to generate a limited number of crossover recombination products on each chromosome, which are essential to ensure faithful segregation of homologous chromosomes. The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans has served as an excellent model organism to investigate the mechanisms that drive and coordinate these chromosome dynamics during meiosis. Here we focus on our current understanding of the regulation of DSB induction in C. elegans. We also review evidence that feedback regulation of crossover formation prolongs the early stages of meiotic prophase, and discuss evidence that this can alter the recombination pattern, most likely by shifting the genome-wide distribution of DSBs.
Keywords: Cell cycle; Chromatin; Chromosome structure; Double-strand breaks; Feedback control; Meiosis; Recombination.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of DSB-1, a protein required for initiation of meiotic recombination in Caenorhabditis elegans, illuminates a crossover assurance checkpoint.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(8):e1003679. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003679. Epub 2013 Aug 8. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23990794 Free PMC article.
-
The C. elegans DSB-2 protein reveals a regulatory network that controls competence for meiotic DSB formation and promotes crossover assurance.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(8):e1003674. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003674. Epub 2013 Aug 8. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23950729 Free PMC article.
-
COM-1 promotes homologous recombination during Caenorhabditis elegans meiosis by antagonizing Ku-mediated non-homologous end joining.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(2):e1003276. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003276. Epub 2013 Feb 7. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23408909 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic recombination in Caenorhabditis elegans.Chromosome Res. 2007;15(5):607-21. doi: 10.1007/s10577-007-1146-x. Chromosome Res. 2007. PMID: 17674149 Review.
-
Checkpoint control in meiotic prophase: Idiosyncratic demands require unique characteristics.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2023;151:281-315. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2022.04.007. Epub 2022 Jun 20. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36681474 Review.
Cited by
-
Crossover patterning through condensation and coarsening of pro-crossover factors.Nat Cell Biol. 2025 Jul;27(7):1161-1174. doi: 10.1038/s41556-025-01688-9. Epub 2025 Jun 19. Nat Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 40537553
-
BRCA1 and BRCA2 Tumor Suppressor Function in Meiosis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 23;9:668309. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.668309. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33996823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic analysis of long intergenic non-coding RNAs in C. elegans germline uncovers roles in somatic growth.RNA Biol. 2021 Mar;18(3):435-445. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1814549. Epub 2020 Sep 5. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 32892705 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic diversity landscapes in outcrossing and selfing Caenorhabditis nematodes.PLoS Genet. 2023 Aug 16;19(8):e1010879. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010879. eCollection 2023 Aug. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37585484 Free PMC article.
-
Leagues of their own: sexually dimorphic features of meiotic prophase I.Chromosoma. 2019 Sep;128(3):199-214. doi: 10.1007/s00412-019-00692-x. Epub 2019 Mar 2. Chromosoma. 2019. PMID: 30826870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keeney S, Giroux CN, Kleckner N. Meiosis-specific DNA double-strand breaks are catalyzed by Spo11, a member of a widely conserved protein family. Cell. 1997;88:375–384. - PubMed
-
- Dernburg AF, McDonald K, Moulder G, Barstead R, Dresser M, Villeneuve AM. Meiotic recombination in C. elegans initiates by a conserved mechanism and is dispensable for homologous chromosome synapsis. Cell. 1998;94:387–398. - PubMed
-
- Baudat F, Frédéric B, Yukiko I, de Massy B. Meiotic recombination in mammals: localization and regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2013;14:794–806. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

