The LATS2 tumor suppressor inhibits SREBP and suppresses hepatic cholesterol accumulation
- PMID: 27013235
- PMCID: PMC4826395
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.274167.115
The LATS2 tumor suppressor inhibits SREBP and suppresses hepatic cholesterol accumulation
Abstract
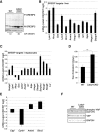
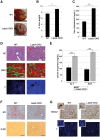
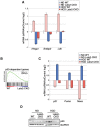
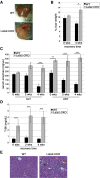
The Hippo signaling pathway is a major regulator of organ size. In the liver, Hippo pathway deregulation promotes hyperplasia and hepatocellular carcinoma primarily through hyperactivation of its downstream effector, YAP. The LATS2 tumor suppressor is a core member of the Hippo pathway. A screen for LATS2-interacting proteins in liver-derived cells identified the transcription factor SREBP2, master regulator of cholesterol homeostasis. LATS2 down-regulation caused SREBP activation and accumulation of excessive cholesterol. Likewise, mice harboring liver-specific Lats2 conditional knockout (Lats2-CKO) displayed constitutive SREBP activation and overexpressed SREBP target genes and developed spontaneous fatty liver disease. Interestingly, the impact of LATS2 depletion on SREBP-mediated transcription was clearly distinct from that of YAP overexpression. When challenged with excess dietary cholesterol, Lats2-CKO mice manifested more severe liver damage than wild-type mice. Surprisingly, apoptosis, inflammation, and fibrosis were actually attenuated relative to wild-type mice, in association with impaired p53 activation. Subsequently, Lats2-CKO mice failed to recover effectively from cholesterol-induced damage upon return to a normal diet. Additionally, decreased LATS2 mRNA in association with increased SREBP target gene expression was observed in a subset of human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease cases. Together, these findings further highlight the tight links between tumor suppressors and metabolic homeostasis.
Keywords: Hippo; Lats; YAP; cholesterol; fatty liver; p53.
© 2016 Aylon et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures



References
-
- Ahrens M, Ammerpohl O, von Schonfels W, Kolarova J, Bens S, Itzel T, Teufel A, Herrmann A, Brosch M, Hinrichsen H, et al. 2013. DNA methylation analysis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease suggests distinct disease-specific and remodeling signatures after bariatric surgery. Cell Metab 18: 296–302. - PubMed
-
- Albanis E, Friedman SL. 2001. Hepatic fibrosis. Pathogenesis and principles of therapy. Clin Liver Dis 5: 315–334. - PubMed
-
- Amaral JD, Castro RE, Steer CJ, Rodrigues CM. 2009. p53 and the regulation of hepatocyte apoptosis: implications for disease pathogenesis. Trends Mol Med 15: 531–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
