Catalytic borylation of methane
- PMID: 27013726
- PMCID: PMC5609458
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aad9730
Catalytic borylation of methane
Abstract
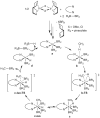
Despite steady progress in catalytic methods for the borylation of hydrocarbons, methane has not yet been subject to this transformation. Here we report the iridium-catalyzed borylation of methane using bis(pinacolborane) in cyclohexane solvent. Initially, trace amounts of borylated products were detected with phenanthroline-coordinated Ir complexes. A combination of experimental high-pressure and high-throughput screening, and computational mechanism discovery techniques helped to rationalize the foundation of the catalysis and identify improved phosphine-coordinated catalytic complexes. Optimized conditions of 150°C and 3500-kilopascal pressure led to yields as high as ~52%, turnover numbers of 100, and improved chemoselectivity for monoborylated versus diborylated methane.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous