Selective Modulation of MicroRNA Expression with Protein Ingestion Following Concurrent Resistance and Endurance Exercise in Human Skeletal Muscle
- PMID: 27014087
- PMCID: PMC4779983
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00087
Selective Modulation of MicroRNA Expression with Protein Ingestion Following Concurrent Resistance and Endurance Exercise in Human Skeletal Muscle
Abstract
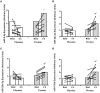
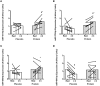
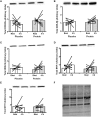
We examined changes in the expression of 13 selected skeletal muscle microRNAs (miRNAs) implicated in exercise adaptation responses following a single bout of concurrent exercise. In a randomized cross-over design, seven healthy males undertook a single trial consisting of resistance exercise (8 × 5 leg extension, 80% 1 Repetition Maximum) followed by cycling (30 min at ~70% VO2peak) with either post-exercise protein (PRO: 25 g whey protein) or placebo (PLA) ingestion. Muscle biopsies (vastus lateralis) were obtained at rest and 4 h post-exercise. Detection of miRNA via quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) revealed post-exercise increases in miR-23a-3p (~90%), miR-23b-3p (~39%), miR-133b (~80%), miR-181-5p (~50%), and miR-378-5p (~41%) at 4 h post-exercise with PRO that also resulted in higher abundance compared to PLA (P < 0.05). There was a post-exercise decrease in miR-494-3p abundance in PLA only (~88%, P < 0.05). There were no changes in the total abundance of target proteins post-exercise or between conditions. Protein ingestion following concurrent exercise can modulate the expression of miRNAs implicated in exercise adaptations compared to placebo. The selective modulation of miRNAs with target proteins that may prioritize myogenic compared to oxidative/metabolic adaptive responses indicate that miRNAs can play a regulatory role in the molecular machinery enhancing muscle protein synthesis responses with protein ingestion following concurrent exercise.
Keywords: adaptation; anabolic; endurance exercise; metabolic; molecular; resistance exercise.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Time Course of Skeletal Muscle miRNA Expression after Resistance, High-Intensity Interval, and Concurrent Exercise.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2021 Aug 1;53(8):1708-1718. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002632. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2021. PMID: 33731656 Clinical Trial.
-
Protein ingestion increases myofibrillar protein synthesis after concurrent exercise.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015 Jan;47(1):82-91. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000000390. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015. PMID: 24870574
-
Regulation of miRNAs in human skeletal muscle following acute endurance exercise and short-term endurance training.J Physiol. 2013 Sep 15;591(18):4637-53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.255695. Epub 2013 Jun 24. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23798494 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA analysis for the assessment of exercise and amino acid effects on human skeletal muscle.Adv Nutr. 2013 Jul 1;4(4):412-7. doi: 10.3945/an.113.003699. Adv Nutr. 2013. PMID: 23858090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs as Biomarkers of Systemic Changes in Response to Endurance Exercise-A Comprehensive Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Oct 13;10(10):813. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10100813. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33066215 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Whey Protein Supplementation Post Resistance Exercise in Elderly Men Induces Changes in Muscle miRNA's Compared to Resistance Exercise Alone.Front Nutr. 2019 Jun 12;6:91. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2019.00091. eCollection 2019. Front Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31249834 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs and Novel Food Compounds Related to the Browning Process.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 28;20(23):5998. doi: 10.3390/ijms20235998. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31795191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Pilot Study of miRNA Expression Profile as a Liquid Biopsy for Full-Marathon Participants.Sports (Basel). 2021 Sep 24;9(10):134. doi: 10.3390/sports9100134. Sports (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34678915 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting Skeletal Muscle Dysfunction and Exercise in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Emerging Significance of Myokines.Aging Dis. 2023 Dec 7;15(6):2453-2469. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.1125. Aging Dis. 2023. PMID: 38270119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PI3K-AKT-FOXO1 pathway targeted by skeletal muscle microRNA to suppress proteolytic gene expression in response to carbohydrate intake during aerobic exercise.Physiol Rep. 2018 Dec;6(23):e13931. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13931. Physiol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30548426 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Coffey V. G., Jemiolo B., Edge J., Garnham A. P., Trappe S. W., Hawley J. A. (2009a). Effect of consecutive repeated sprint and resistance exercise bouts on acute adaptive responses in human skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 297, R1441–R1451. 10.1152/ajpregu.00351.2009 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

