Impact of Background Noise and Sentence Complexity on Processing Demands during Sentence Comprehension
- PMID: 27014152
- PMCID: PMC4785151
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00345
Impact of Background Noise and Sentence Complexity on Processing Demands during Sentence Comprehension
Abstract
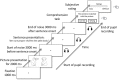
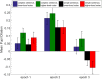
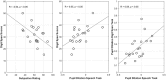
Speech comprehension in adverse listening conditions can be effortful even when speech is fully intelligible. Acoustical distortions typically make speech comprehension more effortful, but effort also depends on linguistic aspects of the speech signal, such as its syntactic complexity. In the present study, pupil dilations, and subjective effort ratings were recorded in 20 normal-hearing participants while performing a sentence comprehension task. The sentences were either syntactically simple (subject-first sentence structure) or complex (object-first sentence structure) and were presented in two levels of background noise both corresponding to high intelligibility. A digit span and a reading span test were used to assess individual differences in the participants' working memory capacity (WMC). The results showed that the subjectively rated effort was mostly affected by the noise level and less by syntactic complexity. Conversely, pupil dilations increased with syntactic complexity but only showed a small effect of the noise level. Participants with higher WMC showed increased pupil responses in the higher-level noise condition but rated sentence comprehension as being less effortful compared to participants with lower WMC. Overall, the results demonstrate that pupil dilations and subjectively rated effort represent different aspects of effort. Furthermore, the results indicate that effort can vary in situations with high speech intelligibility.
Keywords: background noise; digit span; effort; processing demands; pupillometry; reading span; syntactic complexity; working memory capacity.
Figures
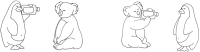


References
-
- Boeg Thomsen D., Kristensen L. B. (2014). Semantic role assignment in Danish children and adults. Acta Linguist. Hafniensia 46 159–198. 10.1080/03740463.2014.990291 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

