The Pokeweed Leaf mRNA Transcriptome and Its Regulation by Jasmonic Acid
- PMID: 27014307
- PMCID: PMC4792876
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00283
The Pokeweed Leaf mRNA Transcriptome and Its Regulation by Jasmonic Acid
Abstract
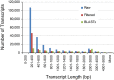
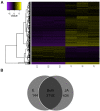
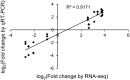
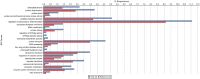
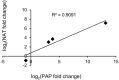
The American pokeweed plant, Phytolacca americana, is recognized for synthesizing pokeweed antiviral protein (PAP), a ribosome inactivating protein (RIP) that inhibits the replication of several plant and animal viruses. The plant is also a heavy metal accumulator with applications in soil remediation. However, little is known about pokeweed stress responses, as large-scale sequencing projects have not been performed for this species. Here, we sequenced the mRNA transcriptome of pokeweed in the presence and absence of jasmonic acid (JA), a hormone mediating plant defense. Trinity-based de novo assembly of mRNA from leaf tissue and BLASTx homology searches against public sequence databases resulted in the annotation of 59 096 transcripts. Differential expression analysis identified JA-responsive genes that may be involved in defense against pathogen infection and herbivory. We confirmed the existence of several PAP isoforms and cloned a potentially novel isoform of PAP. Expression analysis indicated that PAP isoforms are differentially responsive to JA, perhaps indicating specialized roles within the plant. Finally, we identified 52 305 natural antisense transcript pairs, four of which comprised PAP isoforms, suggesting a novel form of RIP gene regulation. This transcriptome-wide study of a Phytolaccaceae family member provides a source of new genes that may be involved in stress tolerance in this plant. The sequences generated in our study have been deposited in the SRA database under project # SRP069141.
Keywords: Phytolacca americana; RNA-seq; jasmonic acid; natural antisense transcript; pokeweed; pokeweed antiviral protein; ribosome inactivating protein; transcriptome.
Figures
References
-
- Ayashi T. H., Obayashi D. K., Ariu T. K., Ahara M. T., Ada K. H., Ouzuma Y. K., et al. (2003). Genomic cloning of ribonucleases in Nicotiana glutinosa leaves, as induced in response to wounding or to TMV-infection, and characterization of their promoters. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 67 2574–2583. 10.1271/bbb.67.2574 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

