Dietary Plant Lectins Appear to Be Transported from the Gut to Gain Access to and Alter Dopaminergic Neurons of Caenorhabditis elegans, a Potential Etiology of Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 27014695
- PMCID: PMC4780318
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2016.00007
Dietary Plant Lectins Appear to Be Transported from the Gut to Gain Access to and Alter Dopaminergic Neurons of Caenorhabditis elegans, a Potential Etiology of Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
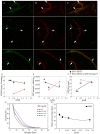
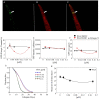
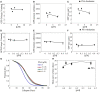
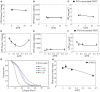
Lectins from dietary plants have been shown to enhance drug absorption in the gastrointestinal tract of rats, be transported trans-synaptically as shown by tracing of axonal and dendritic paths, and enhance gene delivery. Other carbohydrate-binding protein toxins are known to traverse the gut intact in dogs. Post-feeding rhodamine- or TRITC-tagged dietary lectins, the lectins were tracked from gut to dopaminergic neurons (DAergic-N) in transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) [egIs1(Pdat-1:GFP)] where the mutant has the green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene fused to a dopamine transport protein gene labeling DAergic-N. The lectins were supplemented along with the food organism Escherichia coli (OP50). Among nine tested rhodamine/TRITC-tagged lectins, four, including Phaseolus vulgaris erythroagglutinin (PHA-E), Bandeiraea simplicifolia (BS-I), Dolichos biflorus agglutinin (DBA), and Arachis hypogaea agglutinin (PNA), appeared to be transported from gut to the GFP-DAergic-N. Griffonia Simplicifolia and PHA-E, reduced the number of GFP-DAergic-N, suggesting a toxic activity. PHA-E, BS-I, Pisum sativum (PSA), and Triticum vulgaris agglutinin (Succinylated) reduced fluorescent intensity of GFP-DAergic-N. PHA-E, PSA, Concanavalin A, and Triticum vulgaris agglutinin decreased the size of GFP-DAergic-N, while BS-I increased neuron size. These observations suggest that dietary plant lectins are transported to and affect DAergic-N in C. elegans, which support Braak and Hawkes' hypothesis, suggesting one alternate potential dietary etiology of Parkinson's disease (PD). A recent Danish study showed that vagotomy resulted in 40% lower incidence of PD over 20 years. Differences in inherited sugar structures of gut and neuronal cell surfaces may make some individuals more susceptible in this conceptual disease etiology model.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans; dopamine transporter; dopaminergic neurons; fluorescence; plant lectins.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Glycoconjugates in normal human kidney. A histochemical study using 13 biotinylated lectins.Histochemistry. 1988;90(1):51-60. doi: 10.1007/BF00495707. Histochemistry. 1988. PMID: 2466021
-
Lectin histochemistry of pregnant rat uterine tissues.J Anat. 1996 Feb;188 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):197-205. J Anat. 1996. PMID: 8655407 Free PMC article.
-
Subsets of epidermal Langerhans cells as defined by lectin binding profiles.J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Nov;81(5):397-402. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12521995. J Invest Dermatol. 1983. PMID: 6631049
-
Characterization of glycans in the developmental stages of Myxobolus cerebralis (Myxozoa), the causative agent of whirling disease.J Fish Dis. 2007 Nov;30(11):637-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2761.2007.00846.x. J Fish Dis. 2007. PMID: 17958607
-
An anterograde neuroanatomical tracing method that shows the detailed morphology of neurons, their axons and terminals: Immunohistochemical localization of an axonally transported plant lectin, Phaseolus vulgaris-leucoagglutinin (PHA-L).Brain Res. 2016 Aug 15;1645:42-5. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.12.040. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26790346 Review.
Cited by
-
The Gut Microbiome Feelings of the Brain: A Perspective for Non-Microbiologists.Microorganisms. 2017 Oct 12;5(4):66. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms5040066. Microorganisms. 2017. PMID: 29023380 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parkinson disease and the gut: new insights into pathogenesis and clinical relevance.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Nov;17(11):673-685. doi: 10.1038/s41575-020-0339-z. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32737460 Review.
-
The effect of white kidney bean fertilized with nano-zinc on nutritional and biochemical aspects in rats.Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2019 Jun 27;23:e00357. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2019.e00357. eCollection 2019 Sep. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2019. PMID: 31312610 Free PMC article.
-
Purification, Characterization and Bioactivity of a New Homodimeric Lectin From Vicia Altissima (Fabaceae) Seeds.Plant Environ Interact. 2025 Apr 2;6(2):e70047. doi: 10.1002/pei3.70047. eCollection 2025 Apr. Plant Environ Interact. 2025. PMID: 40182644 Free PMC article.
-
Selenium Effects on Oxidative Stress-Induced Calcium Signaling Pathways in Parkinson's Disease.Indian J Clin Biochem. 2022 Jul;37(3):257-266. doi: 10.1007/s12291-022-01031-1. Epub 2022 Apr 15. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35873611 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nachbar MS, Oppenheim JD. Lectins in the United States diet: a survey of lectins in commonly consumed foods and a review of the literature. Am J Clin Nutr (1980) 33:2338–45. - PubMed
-
- Bruylants M, Vennemann M. Le Jequirity. Bull Acad R Med Belg (1884) 3:147
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

