Comparison of Adductor Canal Block and Femoral Nerve Block for Postoperative Pain in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 27015172
- PMCID: PMC4998367
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002983
Comparison of Adductor Canal Block and Femoral Nerve Block for Postoperative Pain in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
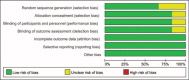
A total knee arthroplasty (TKA) has always been associated with moderate-to-severe pain. A systematic review of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and non-RCTs was performed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pain control of adductor canal block (ACB) and femoral nerve block (FNB) after TKA.Relevant literatures about the ACB and FNB after TKA for reducing pain were searched from Medline (1996-January, 2015), Embase (1980-January, 2015), PubMed (1980-January, 2015), Web of Science (1980-January, 2015), and The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials. High-quality RCTs and non-RCTs were picked to evaluate the visual analogue scale (VAS) and other outcome. This systematic review and meta-analysis were performed according to the PRISMA statement criteria. The software RevMan 5.30 was used for the meta-analysis.Eight literatures fitted into the inclusion criteria. There were no significant differences in VAS score with rest or mobilization at 4, 24, and 48 h between ACB group and FNB group. There were also no significant differences in the strength of quadriceps and adductor, the length of hospital stay, and complications of vomiting and nausea.Present meta-analysis indicated that ACB shows no superiority than FNB group. Both of them can reduce the pain score after TKA. As referred to which method to adopt, it is determined by the preference of the surgeons and anesthesiologists.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

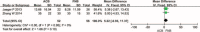






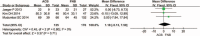

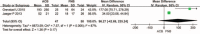


Similar articles
-
Is Adductor Canal Block Better Than Femoral Nerve Block in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty? A GRADE Analysis of the Evidence Through a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Arthroplasty. 2017 Oct;32(10):3238-3248.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2017.05.015. Epub 2017 May 17. J Arthroplasty. 2017. PMID: 28606458
-
Comparison of local infiltration analgesia and sciatic nerve block as an adjunct to femoral nerve block for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 May;96(19):e6829. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006829. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28489762 Free PMC article.
-
Adductor canal block provides better performance after total knee arthroplasty compared with femoral nerve block: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Orthop. 2016 May;40(5):925-33. doi: 10.1007/s00264-015-2998-x. Epub 2015 Oct 10. Int Orthop. 2016. PMID: 26452678
-
The comparison of adductor canal block with femoral nerve block following total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review with meta-analysis.J Anesth. 2016 Oct;30(5):745-54. doi: 10.1007/s00540-016-2194-1. Epub 2016 Jun 4. J Anesth. 2016. PMID: 27262287
-
Combined femoral and sciatic nerve block versus femoral and local infiltration anesthesia for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Orthop Surg Res. 2016 Dec 7;11(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s13018-016-0495-6. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016. PMID: 27923404 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Overview of Total Knee Arthroplasty and Modern Pain Control Strategies.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2016 Nov;20(11):59. doi: 10.1007/s11916-016-0592-6. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2016. PMID: 27655139 Review.
-
Liposome bupivacaine for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2016 Jul 22;11(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s13018-016-0420-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016. PMID: 27443874 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of adductor canal block versus femoral nerve block in patients with anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Sep;98(36):e16763. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016763. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31490364 Free PMC article.
-
The efficiency and safety of oral tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Nov;98(46):e17796. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017796. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31725622 Free PMC article.
-
Motor-Sparing Effect of Adductor Canal Block for Knee Analgesia: An Updated Review and a Subgroup Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Based on a Corrected Classification System.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jan 10;11(2):210. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11020210. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36673579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singelyn FJ, Deyaert M, Joris D, et al. Effects of intravenous patient-controlled analgesia with morphine, continuous epidural analgesia, and continuous three-in-one block on postoperative pain and knee rehabilitation after unilateral total knee arthroplasty[J]. Anesthesia and analgesia 1998; 87:88–92. - PubMed
-
- Paul JE, Arya A, Hurlburt L, et al. Femoral nerve block improves analgesia outcomes after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Anesthesiology 2010; 113:1144–1162. - PubMed
-
- Sato K, Adachi T, Shirai N, et al. Continuous versus single-injection sciatic nerve block added to continuous femoral nerve block for analgesia after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, double-blind study[J]. Regional Anesth Pain Med 2014; 39:225–229. - PubMed
-
- Fowler SJ, Symons J, Sabato S, et al. Epidural analgesia compared with peripheral nerve blockade after major knee surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials[J]. Br J Anaesth 2008; 100:154–164. - PubMed
-
- Fischer HB, Simanski CJ, Sharp C, et al. A procedure-specific systematic review and consensus recommendations for postoperative analgesia following total knee arthroplasty[J]. Anaesthesia 2008; 63:1105–1123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

