Immune thrombocytopenia after bee venom therapy: a case report
- PMID: 27015661
- PMCID: PMC4807563
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-016-1091-3
Immune thrombocytopenia after bee venom therapy: a case report
Abstract
Background: Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is a hematological disorder with an isolated decrease in number of circulating platelets. Bee venom therapy (BVT) is a form of alternative medicine. It is still being practiced in the Middle East and other parts of Asia. In BVT, acupuncture points are used to inject diluted bee venom into the body. The pharmacological basis behind BVT is not fully understood. However, it has been used to treat various medical conditions such as arthritis and low back pain. On the other hand there have been a number of reported complications of BVT use such as ITP. We present a case report on ITP after BVT.
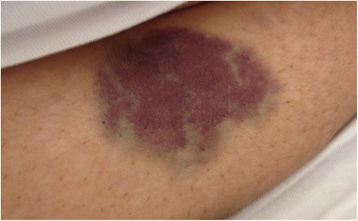
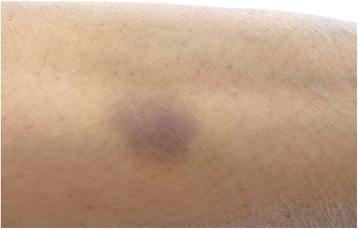
Case presentation: A 61 year old lady presented with gum bleeding and ecchymosis and found to have isolated thrombocytopenia (platelet count of 9 × 10(9)/L) after receiving four direct bee sting sessions. There was no evidence of any other risk factors of ITP.
Conclusion: Bee venom components and toxicity may be associated with thrombocytopenia as a complication. Further research is needed to postulate guidelines and protocol for BVT. In the meantime, monitoring of the practice of BVT should be made, with an emphasis on patient education regarding the safety profile and associated risks compared to the gained benefits.
Keywords: Acupuncture; Bee; Complication; Hematology; Immune; PLA2; Therapy; Thrombocytopenia; Venom.
Figures
References
-
- Rodeghiero F, Stasi R, Gernsheimer T, Michel M, Provan D, Arnold D, Bussel J, Cines D, Chong B, Cooper N, Jodeau B, Lechner K, Mazzucconi M, McMillan R, Sanz M, Imbach P, Blanchette V, Kuhne T, Ruggeri M, George J. Standardization of terminology, definitions and outcome criteria in immune thrombocytopenic purpura of adults and children: report from an international working group. Blood. 2009;113:2386–2393. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-07-162503. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Johnsen J. Pathogenesis in immune thrombocytopenia: new insights. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2012;2012:306–12. - PubMed
-
- Frederiksen H, Schmidt K. The incidence of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in adults increases with age. Blood. 1999;94:909–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials